5 Primates
Phil Geib; Bill Belcher; and Timothy Sefczek
Learning Objectives
This chapter’s learning objectives include:
- How do primates differ from other mammals?
- What distinguishes humans from other primates?
- When, where, & why did early primates emerge?
- How & why did they diverge?
Most primates live in the tropics and indeed tropical forests were the setting of their evolution, which began around 66 millions years ago at the Cretaceous–Tertiary boundary when dinosaurs went extinct. A few species of monkeys (snub-nosed and macaques) have expanded into areas of cold and snow in Asia and Japan. You’ve probably seen pictures of Japanese macaques, or snow monkeys, sitting in hot pools with their heads covered with frost or snow. Humans are the only primate capable of living in virtually any environment of the world, all because of culture, our learned behaviors.
Humans belong to the order Primates. All living primates, including humans, evolved from earlier primates that are now extinct. There are over 500 primate species in the world today, all grouped together as members of this biological order. The primate order contains all the species commonly related to the lemurs, monkeys, and apes, with humans included in the latter category.
Primatologists study the evolution, anatomy, and behavior of nonhuman primates (hereafter primates). Studying primates (primatology) is inherently interesting to some because of obvious similarities of these animals to us. Indeed, anthropologists were traditionally interested in studying primates with adaptations most similar to our own. This meant primates living on the ground rather than in trees – terrestrial monkeys and terrestrial apes – and mainly in primates most closely related to us, especially chimpanzees and bonobos. And one of the major goals in primatology is to help understand human evolution and human nature.
It is because of this connection between primates and humans that some primatologists are trained in anthropological departments as biological anthropologists. However, some train in other disciplines such as biology or ecology. For example, Robert Sapolsky is a world-famous primatologist and professor of Neurology and Neurological Sciences at Stanford University. He has spent some 30 years studying a troop of baboons in Africa and the role that stress plays in health outcomes.
Intensive field research of primates in wild settings began in the 1960s. This is when Jane Goodall began her long-term study of chimpanzees. She made some remarkable discoveries and helped to usher what might be termed primate ethnography, becoming embedded within a primate social group so as to witness behavior in a very up-close and personal way.
Most primates have very long lives. Baboons live for about 25 years on average and chimpanzees for about 50 years. This means that field studies must occur across decades to provide a comprehensive understanding. Research programs were established that have enabled data to be collected on specific troops of baboons, chimps and other primates across 40 years and growing. This is important because primates adapt and adjust their behaviors as the environment around them changes, and we can always learn something new.
Behavioral Ecology is a primary theoretical orientation for understanding primate behavior. The basic question posed by this approach is this: How does the environment that a species lives in shape its behaviors? A similar question also gets considered in an evolutionary framework by those studying fossil primates: How might the past environment that a species lived in shape their anatomical and other adaptations?
Common Primate Traits
If you saw the following multiple-choice question on an exam what answer would you choose?
Question: Key adaptive traits of primates include which of the following?
a) Bipedalism and grasping hands (opposable thumbs)
b) Bipedalism, grasping hands, and forward-facing eyes
c) Grasping hands, forward facing eyes, and nails.
d) Grasping hands, forward facing eyes, collarbone, and language.
Give yourself a point if you selected (c) on this list. Bipedalism is key for humans, but we are the only living primate that has this trait. It was a rather late development for the primate lineage and all other bipedal primates are now extinct. Language is also rather unique and an even later development.
Several traits are shared by all primates. Some of these are the ones that Linnaeus specified as the features that distinguish all primates from other animals. The first three in the list below are the distinguishing traits; the others are important primate adaptations but are found in other species as well.
-
Grasping hands (& feet) made possible by opposable thumbs (and opposable big toe).
-
Nails. All primates have evolved to have nails on their fingers and toes instead of claws (though some have re-evolved claw-like nails for specialized feeding behaviors).
-
Specialized location of ear bones (petrosal auditory bulla). Only primates have their inner ear bones located in this part of the skull.
-
Large brained relative to body size. This trait is thought to arise in large part from the living in social groups.
-
Social living (but with a few exceptions, such as orangutans, largely on account of food resources being too sparse and widely scattered).
-
Stereopsis, which means vision with depth of field perception (color vision is common)
-
Omnivorous (also with some exceptions of species that specialize is specific foods such as the gelada baboon).
Common primate skeletal features mostly reflect an arboreal adaptation, a heritage of life in trees. Climbing by grasping with prehensile hands and feet is a fundamental adaptation of primates. Living in trees helped to reduce predation and trees provided abundant food in the form of flowers, fruits, nuts, and insects. Collarbones, common in mammalian ancestors but absent in some modern mammals (like horses), provide great freedom of shoulder movement, a key aid in tree canopy living. Stereoscopic vision allows depth perception to judge branch to branch distance.
Improved infant survival necessitated longer lifespan in primates. However, with longer lifespans came increased developmental periods and dependence on parents. This placed more emphasis on single reproduction events: offspring quality over offspring quantity. Primates mostly follow the ‘one-half rule’, according to which the average number of young in a litter is one half the typical number of mammaries. Humans conform to the rule: two breasts and typically just one infant.
The common primate skeletal features highlight an important concept in evolution known as Romer’s Rule. This rule can be paraphrased as follows:
important evolutionary changes often enable organisms to continue their same way of life, rather than to adapt to a new one.
But, a trait that evolves to maintain an existing life form can ultimately play a major role in changing that life form. This is why the current utility or function of a trait (including behavior) might have nothing to do with why that trait or behavior appeared in the first place. Our opposable thumbs allow us to manipulate tools, but this is not why the grasping hand appeared in the first place. It was a fortuitous outcome that eventually allowed tool use, and this altered our evolutionary trajectory. A biological term for this is exaptation.
The primate hand (and foot) is evolved for grasping, being extremely flexible and prehensile. All primates have retained five digits on hand and foot except three groups (spider monkeys and muriqui of South America and the colobus monkeys of Africa). The thumb is absent or reduced in these exceptions, evidently as an adaptation for moving in trees. Primates also have broad, flat nails instead of claws. Nails (or rather the bone that supported these perishable features) are key for demonstrating that a new way of locomotion has evolved. No more skittering around using claws like squirrels do. There were now sensitive tactile pads on fingers, toes, heels, and palms for gripping and touch. These tactile pads, especially in the fingers, are enriched with sensory nerve fibers. Opposable thumbs (and big toes) allow for precise and powerful grip. Some primates only have a power grip, but some developed a precision grip; this trait became the most developed in humans. The reasons for the initial evolution of these adaptations is unknown, but primates have used these adaptations to successfully fill their own ecological niche.
There are several secondary effects of the grasp hand. The hand becomes the organ of foraging, bringing food to the mouth. Some primates might also clean food prior to bringing it to their mouth. Harvesting food then bringing it to the mouth places an emphasis on hand-eye coordination, something that eventually becomes quite important for tool use with humans.

Grasping hands allow many primate infants to cling to mom. Though not all infants hold onto mom, in those that do, clinging appears to be an instinctual behavior. Most moms need to move with their social group and feed; those that do frequently have babies that cling on their back or stomach. It’s a survival mechanism: cling or die and the trait for those that cannot cling is soon extinguished. Clinging also helps babies maintains a relationship with mother. By clinging to mom, infants learn valuable lessons about their world:
-
What to eat and what not to eat.
-
When and where foods will be available.
-
How to avoid predators
-
What vocalizations to use and when.
The precision grip and hand-eye coordination allows for grooming. This is key to social interactions for primates. It is pleasurable to the groomed and the groomer. This pleasure has been measured both by a drop in blood pressure and release of the hormone called oxytocin. This hormone plays a role in forming social bonds since both the groomer and the groomed get a hormonal dose of oxytocin.
Opposable big toes, like opposable thumbs, enable a firm grasp by nonhuman primates. A chimpanzee foot looks more like our hands than our feet. We lack this feature due to our bipedal adaptation, something that developed rather late in ape history, only some 4 million years ago. It is theorized that apes evolved to hang and swing from branches in the trees as that allowed them to get to ripe fruit faster. But as the environment changed and the forest canopy broke up, some apes became adapted to living on the ground. In a quintessential example of Romer’s Rule, bipedal movements that evolved with some ancestral apes in trees (walking bipedally along boughs like gibbons), becomes a boon for terrestrial living, eventually leading to the reorientation of the big toe such that it was no longer opposable. This feature was common among several species of human-like primates after the split from chimpanzees, but now humans are the only surviving species with this trait.
An enhanced sense of vision is an evolved key adaptive trait for primates. Convergence of the eyes provides significant overlap in the visual fields, stereoscopic vision, and this allows for accurate depth perception. The ability to judge depth accurately is important for species moving about in the trees, especially in jumping or swinging from branch to branch. Individuals lacking an ability to determine distance will fall if moving quickly as when trying to avoid a predator, whereas those with the ability would persist to pass on the trait.
Stereoscopic vision requires forward-facing eyes, a trait that is widespread in the animal kingdom among predators. So, this is yet another beneficial aspect of enhanced vision the ability to focus carefully on prey, whether that be a moving insect or even a fruit, nut, or flower. In primates forward-facing eyes were accompanied by having eye orbits structurally supported by a bony ridge along the outside of the eye, which helps to protect this important organ. Most mammals, such as the raccoon, have an open eye orbit, with no bone surrounding it at the side. This allows eyes to rotate backward providing for considerable peripheral vision without head movement. As primates evolve, visual acuity becomes even more pronounced in monkeys and apes, at which point the orbit evolves to have bone around the rear of the eye as well as along the side.
Most primates have color vision which is comparable to the color vision in birds. Color vision occurs in all primates that are diurnal, which is most of the order, and also in some of the nocturnal strepsirrhines (lemurs and lorises). Color provides for a more differentiated world. Greater differentiation of reality helps with predator and food detection by breaking up camouflage. It helps with depth perception and is critical for locating and judging the ripeness of fruits and vegetation that is higher in nutrition. Color also allows for detecting sexual displays. Monkeys are the mostly vividly and distinctly colored of all mammals. This likely would not have occurred without color vision.

For most primates, the visual sense developed at the expense of the olfactory sense. Most primates have a reduced sense of smell, something that is reflected in the smaller and less projecting snouts. The reduction of the snout actually helped the eyes to rotate further forward for enhanced binocular vision. Along with the reduction in snout size, there was a loss of the wet nose, or rhinarium . Animals that have this feature usually have a keen sense of smell, like dogs do.
The wet nose/dry nose split is used in primate taxonomy with dry nose primates, named haplorhines (this includes tarsiers, monkeys, and apes), and wet nose primates, named strepsirrhines (this includes lemurs, lorises, and galagos). All haplorhines have a nose that is dry on the outside, wet on the inside. Strepsirrhines retained the wet nose and this reflects a continued emphasis on smell. They have special scent glands and do considerable tree marking with these glands, so it’s no wonder that they retained the olfactory emphasis and wet nose. Many other mammals depend on sent marking to send messages, such as dogs and cats.
Primate brain morphology can also differ, especially with the shrinking olfactory bulb: it’s relatively large in strepsirrhines, but nowhere near as large as in a dog. The bulb is far less pronounced in monkeys than strepsirrhines and relatively tiny in apes. Conversely the occipital lobe expanded. This back part of the brain is involved with vision. There is a significant change from strepsirrhines to monkeys in this feature and it is even more developed in apes, such as chimps.
Among primates, the great apes have the largest and most complex brains, while strepsirrhines have the smallest and least complex. Chimps and other apes exhibit a huge expansion in the parietal lobe. This part concerns the processing of sensory information including such tasks as spatial organization and navigation. Humans top the primate list for brain complexity and size. This doesn’t mean we are tops in the animal kingdom since cetaceans (whales & dolphins) might have us beat. Nor can we easily translate this for comparison of intelligence. For instance, chimpanzees, though possessing a smaller and less complex brain than humans, are better able to remember when and where food is located in a forest. This type of intelligence is reflective of ecological stimuli they contend with in order to survive, stimuli we fortunately encounter much less frequently.
The morphology and proportions of primate limbs depends on whether a species is adapted to living in the trees or to life on the ground. Terrestrial or ground-dwelling primates includes some old world monkeys, like baboons and macaques, all African great apes (i.e., gorillas, bonobos, chimpanzees), and humans. Arboreal or tree-dwelling primates include all strepsirrhines, tarsiers, New World monkeys, many Old World monkeys, and three apes: gibbons, siamangs, and orangutans.
New World monkeys are the most highly adapted to life in the trees and there are no ground dwelling species. They have become so specialized to tree life that some have developed prehensile tails, a 5th appendage to help hold onto branches. Indeed, there are so many arboreal primates that they have filled different ecological niches to avoid competing with each other. Marmosets and tamarins have reduced in size and evolved claw-like nails to feed on tree sap, saki monkeys have evolved specialized teeth to crack open hard nuts, and capuchin monkeys have evolved large brains to extract resources from protected structures, like clams from shells or kernels from hard nutshells.
If you were asked a trivia question about whether both monkeys and apes knuckle walk how would you answer? Knuckle walking is a form of four-legged locomotion whereby individuals walk on the soles of their feet but not on the palms of their hands. Rather, they bend their fingers and support the head end of their bodies with their knuckles. Monkeys do not knuckle walk. Only apes do this: think gorillas, chimpanzees & bonobos.
The primary modes of primate locomotion include the following:
-
Arboreal quadrupedal slow climbing (e.g., lorises, pottos)
-
Arboreal quadrupedal fast climbing and leaping (e.g., colobus, langur)
-
Arboreal forelimb brachiation/suspensory (e.g., spider monkey, gibbon)
-
Terrestrial quadrupedalism (e.g., baboons, macaques)
-
Terrestrial quadrupedalism by knuckle-walking (e.g., chimps, gorillas)
-
Terrestrial bipedalism (humans are the only extant example)
-
Vertical clinging and leaping on trunks (e.g., tarsiers, sifakas)
Humans retain some ability for suspensory locomotion, but it’s a far cry from the ability of true arboreal apes such as gibbons. We now use the flexibility of our shoulders for pursuits that pay even high rewards than harvesting fruit: pitching in the MLB or throwing a football in the NFL.
Common primate dental features mostly reflect an omnivorous diet—the eating of many different foods: insects and other arthropods, small reptiles and mammals, and various plant parts such as fruits, seeds, leaves, stems, roots, and gums or sap. With a true omnivore, like humans, nearly everything can be on the table. Omnivory in primates is possible because of their four functional tooth types: incisors, canines, premolars, and molars.
- Molars & premolars are unspecialized (generalized for omnivorous diet)
- incisors & canines, the front teeth, are often very specialized, particularly in the lower primates (e.g., dental comb among some strepsirrhines).
Primate Classification
Surprisingly, new primate species are still being discovered. Approximately 44 species of primate were newly described between 2010 and 2020. Hlaf of these new species were nocturnal strepsirrhines. The reason for this increase in species identificaiton is largely due to a change in how we are identifying species. Historically, species were labeled based on phenotypic differences, those that can be seen with the naked eye. However, many of the nocturnal strepsirrhines look the same – small, arboreal, and brown fur color. It is only through a combination of genetic analysis, understanding of ecological/behavioral nuances, and calculated differences in skeletal measurements that we have been able to tease apart these visually similar-looking species. This is even true of some diurnal species, such as the recently (2017) identified Tapanuli orangutan, which looks like its neighbor the Sumatran orangutan, but is genetically distinct.
Biological classification has changed in recent years because of DNA research. There has been considerable readjustment for some lifeforms as data have poured in, but genetic results for primates generally supports traditional morphological classifications. Primate classification could shift some still, but there is a basic grouping that is unlikely to change. The first major split in the system is essentially between wet and dry nosed primates (strepsirrhine and haplorhine). This was already discussed previously. Wet nose, or rhinarium, indicates a greater use of smelling sense. The wet nosed primates are known as Strepsirrhini. This includes all lemurs of Madagascar, the bushbabies and pottos of Africa, and the lorises of India & southeast Asia. These individuals retain numerous ancestral traits, those that the earliest primate ancestors would have had, including a grooming claw on their big toe, a tooth comb, a reflective surface behind the eyes (called a tapetum lucidum), and of course a rhinarium.
The oddball of the primate order are the tarsiers of Southeast Asia. Though they have retained some primitive characteristics, such as a grooming claw, but have far more derived characteristics, or those that have changed since the earliest primates. Derived features are consistent in all other haplorhines and include the absence of a grooming claw, the lack of a tooth comb, no tapetum lucidum, and a dry nose. Tarsiers overwhelmingly have derived traits, thus their inclusion in the haplorhines, but still retain one or two ancestral ones, making them historically tougher to categorize.
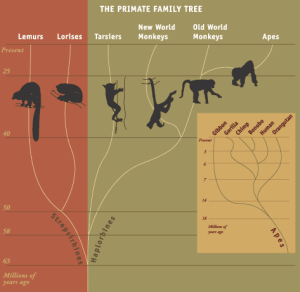
The second major split in the system is with haplorhines and distinguishes the New World and Old World primates. Nose shape serves as the distinguishing trait in this instance. Their overall group name reflects this: Platyrrhini for New World primates means flat-nosed. They have nostrils that face sideways. Catarrhini for Old World primates have nostrils that face downwards like this grinning macaque on the Indonesian island of Sulawesi. Humans obviously have downward noses, as do all apes, which means they are part of the catarrhini. When you next go to a zoo and look at some monkeys you should be able to tell whether they are Old World or New World by nose shape. Perhaps you might not be able to get close enough to see there noses but there is another way to tell at at least for some monkeys. If you saw them hanging upside down by their tails, would that be a New World or Old World monkey? If you guessed New World monkey then give yourself a point. Old World monkeys lack a prehensile tail. Another distinctive feature, and one most often used in differentiating fossil platyrrhines from fossil catarrhines, is the number of premolars. Platyrrhines have three premolars, while catarrhines only have two, losing one through evolutionary processes.


Another visual trait that is prominent in Old World monkeys is sexual dimorphism. Many Old World monkeys have considerable sexual dimorphism, with males being larger in body size than females and sometimes having other distinctive features. This trait is especially true for those Old World monkeys that live life mostly on the ground rather than in the trees, think baboons. Recall that all New World monkeys live in the trees and they tend to have significantly less sexual dimorphism. Traits that accompany the greater size of Old World monkey males include distinctive and highly colorful hair and skin (sometimes including manes) and frighteningly large canines as shown in this image for a gelada baboon.
There is a correlated aspect to the relative degree of sexual dimorphism that exists between New World and Old World monkeys: Most Old World monkeys have considerable sexual dimorphism and they do not form pair bonds, indeed the mating systems are usually polygynous or polygynandrous . Even for New World monkeys, those that are the most sexually dimorphic follow one of these matting patterns.
What might be the evolutionary reason for the correlation in primates between greater size differences and whether or not males and females pair bond? Which would you think was the dependent variable and which the independent variable? Does sexual dimorphism result in a lack of pair bonding? Or is the converse true: Does forming pair bonds select for (result in) less sexual dimorphism? Key to this is to think about the functional evolutionary role behind larger male body size and the other traits such as massive canines. Why did sexual dimorphism evolve in some primate species and in many other animal species? This relates to male-male (intrasexual) competition over reproductive access to females. Large body and canines size are the tools used in such competition both in actual physical contests and in displays, which is what the male gelada is doing in the above image. Getting back to the original question, pair bonding reduced the advantage of exceptionally large males because male-male competition over females was lessened.
The third major classificatory split in primate lineage is between Old World monkeys (Cercopithecoidea) and apes (Hominoidea). One easy way to tell the difference between an ape and monkey, and indeed one of the distinguishing traits, is that monkeys have a tail and apes do not. Just think of your own back side. At a zoo if you see some primate and it lacks a tail then you know immediately that it is an ape and not a monkey. The one semi-exception to this is the Barbary macaque of north Africa (and introduced historically to Gibraltar), which has a vestigial tail. Gibbons are the smallest apes and might be mistaken for monkeys, especially since they live an arboreal life and excel at swing from tree branches, but the lack of a tail gives them away.
Strepsirrhines
Strepsirrhines are a group of primates that includes all those with a wet-nose, such as lemurs, galagos, and lorises. All members of this group, no matter the species are considered to have characteristics that are more “primitive,” which means more like how all primates looked early in their evolutionary history, some 60-65 million years ago. This does not mean that strepsirrhine species stopped evolving since this process never stops. It means that the modern strepsirrhines more closely resemble early primates at a time in our evolutionary history well before any monkeys or apes were present.
Strepsirrhines are a diverse group in morphology, behavior, adaptive strategy, and body size, at least with the lemurs on Madagascar. All strepsirrhines are primarily arboreal, and the vast majority are nocturnal. They are omnivorous but tending to eat high nutrition items such as small animals and plant fruits and gums (fauni-frugivores). One of the most unusual species of this group is the aye-aye discussed in the video below, which has a highly specialized diet and corresponding adaptations of teeth and hands.
Another interesting part of the strepsirrhine group are the slow lorises in the genus Nycticebus that produce a venom by licking a special gland on the inside of the elbows and mixing it with saliva. This mixture is used for at least three purposes: to defend against parasites (think bug spray), as a protection in fights with other slow lorises (think mace but applied via a bite), and to protect the young, especially when mothers leave the nest, leaving them vulnerable (she licks their fur, covering them with the venom/saliva mixture prior to leaving). Slow loris venom can kill humans through anaphylactic shock or result in scarring. Unfortunately, the unbelievable cuteness of lorises makes them subject to illegal pet trade that causes suffering as their teeth are removed to prevent them from biting people. Wild animals, no matter how cute, are not pets.
Tarsiers
As mentioned before, tarsiers are a taxonomic enigma. Retaining several ancestral traits and evolving multiple derived features, tarsiers have been a difficult species to classify since their introduction to science in 1705. The family Tarsiidae contains three genera and 14 species of tarsier. All tarsiers are found in Southeast Asia (Philippines, Indonesia, Papua New Guinea). Tarsiers are small bodied, nocturnal, and the only completely faunivorous primate, mostly consuming insects but also sometimes small birds and reptiles. Tarsiers do not have a rhinarium so their sense of smell is not as good as the strepsirrhines, and they have evolved to have no tapetum lucidum (reflective surface) behind their eye. Being nocturnal, these adaptations could be seen as detrimental to their survival. But tarsiers found another solution: big eyes! Each tarsier eye is bigger than its brain! In addition to large eyes, tarsiers have evolved incredible leaping abilities. These 150 g (5 ounce) animals can jump upwards of 10 feet! With large eyes that can see all movement and being able to jump incredible distances, most insects are not able to escape a hungry tarsier.
New World Monkeys
Besides nose shape and nostril position, New World monkeys (Platyrrhini) have these other common features:
- 3 premolars, instead of 2 as with Old World monkeys and apes.
- Some species have a prehensile tail, such as the howler & spider monkeys.
- All are arboreal (there are no exceptions).
Some New World monkeys never or rarely come down out of the trees. Some, such as capuchin monkeys, come down for specific things, but then quickly retreat to the branches.

Capuchin monkeys are tool users, the only New World monkeys currently known to do so. Both robust (genus Sapajus) and gracile (genus Cebus) capuchins use rocks to crack nuts, doing this on the ground. This is a main reason that they spend time out of the trees. This is learned behavior and adolescents learn how to perform this feat by observing adults that are highly proficient. Studies show that when processing cashew nuts the monkeys are selective in the rocks chosen and match nut ripeness. These nuts have a protective caustic resin (this is the same plant family as poison ivy!) in the outer shell that can cause severe allergic reactions. Capuchin monkeys provide another demonstration that human tool use is not exceptional and that other primates, indeed other animals (think crows and sea otters), have a type of learned tool use “culture”. Curiously, a capuchin’s tool-using capacity is similar to that of chimpanzees despite having diverged in evolutionary history some 40-35 million years ago. This does not mean that tool use was present back then, but that the cognitive ability for doing so evolved independently in both New World and Old World primates (convergent evolution). Capuchin tool use dates back at least 3000 years, so that is a persistent learning tradition. What remains to be determined is whether or not they learned this behavior for themselves or by copying humans. Even if it resulted from copying, the achievement is still impressive and it has been passed on for 100s of generations.
Marmosets & Tamarins
One large family (Callitrichidae) of New World monkeys includes the marmosets and tamarins. There are eight genera and about 51 species. All are quite small, about squirrel size. They mostly eat insects and tree exudates. They tend to have either a mated pair (monogamy) or a female mated to more than one male (polyandry). Marmosets and tamarins tend to have multiple births, often twins. This would be the equivalent of a human having two 15-pound babies! It is because of the energetic investment of caring for twins that males of this group actually help in child rearing by carrying the young. Known as male parental investment , this is a key adaptive trait in some primates. Male parental investment ranges on a continuum, with humans at the far extreme end of high investment, likely one of the significant traits that allowed the human lineage to be so successful.
Other New World Monkeys
In addition to the Callitrichidae, biologists now commonly recognize 4 other families of New World monkeys. The night or owl monkeys are in a family (Aotidae); capuchins and squirrel monkeys in a second family (Cebidae); howler monkeys, spider monkeys, woolly monkeys, and muriqui in a third family (Atelidae); the fourth family (Pitheciidae) consisting of titi monkeys, saki monkeys, & uakaris.
These monkeys have one offspring at a time and females in most cases bear the costs of parental care; exceptions include the monogamous night monkeys and titis. The diet for most species consists of insects and other small animals, flowers, fruits, and nuts (fauni-frugivores), with howler monkeys also including leaves (being mostly folivores). Life in the trees also tends to be safer from predators, except for humans. The larger New World monkeys (howlers especially) were and are a food item for Indigenous Americans.
One distinct aspect of New World monkeys is that most species typically lack full color vision (trichromacy) especially males, instead seeing the world in two colors (dichromacy). Howler monkeys are an exception to this pattern and see the world in full color. In dichromatic species males always have this trait but some females are heterozygous for the single X chromosome gene that is key in color vision allows them to see with trichromatic vision. New World monkeys are useful research subjects when it comes to understanding and evaluating the adaptive significance of three color vs. two color perception of the world.
Old World Monkeys
Baboons, Mandrills, Drills, & Geladas
Many baboons (genus Papio) live in African savannas and this was thought to be similar to the sort of environment that human ancestors evolved in. Consequently, research with baboons was driven by evolutionary considerations with the goal of understanding how humans evolved. The primates included in this group are the largest of the Old World monkeys and almost exclusively occupy Africa; one baboon species is native to the Arabian Peninsula (no baboons occur in Asia). They are ground dwelling (terrestrial) and diurnal primates with baboons and geladas occupying rather open habitats. Researchers have gained considerable knowledge about baboon and gelada behavior in large part because their open habituate makes for easy observation.

Because of their local ecologies, mandrills and drills also commonly forage on the ground in forests. Despite being primarily terrestrial, all species retreat to trees or rocky outcrops at night as a defense against predators. All species have hairless pads of skin on their protruding buttocks called ischial callosities that provide for sitting comfort, like having butt callouses. All species exhibit significant sexual dimorphism in size of body and canine teeth and some other features such as coloration. The mandrills are the most distinctive in this aspect with the brightest coloration an indicator of male dominance rank, which correlates with male mating success in their polygamous primate groups. All species of this group live in multi-male multi-female social groups that can be quite large, numbering into the hundreds of individuals. For baboons these groups are called troops but with mandrills the term hoard is used. The rather complex social structure for geladas has small size reproductive units nested within bands clustered within herds. Large social group helps both in defense of territory from conspecifics and in defense against predators. The mating system in all cases is polygamous with some males achieving great reproductive success while other males do not.

All of these species, especially male individuals, have a relatively long snout, which might seem to imply that they rely more on smell; yet they lack a rhinarium . The snout remains large with this group of primates because of their oversized canines. Canines are an important trait in males for reproductive competition–fighting with fellow males in their social groups. As mentioned, these primates live in multi-male, multi-female group. A mature male might eventually acquire their own harem of females but to do so requires intense competition with rival males. Males use their huge canines for posturing and offense in fights to gain access to females (male-male competition). Enlarged canines have evolved under sexual selection, which is driven by female choice. Males with the largest canines tend to have greater dominance and therefore are preferred by females, thus affording them larger harems and the opportunity to sire more offspring. The large gap between incisors and premolars, called a diastema, accommodates these massive canines so the mouth can fully close.
Other Old World Monkeys
Most of the other Old World monkeys are smaller in size than the previously considered group and are widely spread across tropical and subtropical areas of Asia in addition to Africa. Many are arboreal with some that are largely folivorous, while others are largely frugivores, through supplemented with occasional insects or small animals. There are at least 20 genera and numerous species with some being quite widespread and frequently interacting with humans, such as macaques (genus Macaca) and the Gray langur (genus Semnopithecus). One macaque species lives in the wild on Gibraltar (the Barbary macaque, Macaca sylvanus), the only monkey species in Europe and evidently escaped from animals introduced from Morocco by Muslims during their conquest of the Iberian Peninsula during the 8th century. The native habitat of this macaque is in the mountains of Morocco of north Africa. This is the only species of macaque outside of Asia.

Some of the species have unique features such as the proboscis monkey (Nasalis larvatus) shown here, which is one of the largest monkeys native to Asia. With this species, size does matter for males since those with bigger noses attract more females to their harems (the large nose is just one of the sexual dimorphic features of this species). This monkey is also a good swimmer, even under water, although this can be dangerous because of crocodiles.
A unique aspect occurs in the largest guenon species (Cercopithecus neglectus), one that reaches a weight of 7 kg for males, has pair-bonding as a common behavioral aspect, and yet presents considerable sexual dimorphism. This is counter to the usual pattern in primates generally and most of the other diverse species lumped here which are sexual dimorphic and have polgynous mating systems. In such systems it is rather common for adult males to practice infanticide in order to return females into estrus. This is an evolved behavioral strategy that occurs when a new male takes over a troop. The infants do not possess his genes and his tenure is potentially short, so the more females that he can impregnate, the larger his genetic legacy.
As a scientist studying this behavior, this is when you need to clearly distinguish between fact and value: you shouldn’t let your desire about what you wish were true affect your judgment about what is true and what the causes are. Labeling adult male monkeys as psycho-killers or monkeys gone bad provides no understanding of the behavior, it is a value judgement that comes from your place in human society. Understanding the evolutionary basis behind behavior demands setting aside the value judgements. This can be easy when researching monkeys but when it comes to that other primate, humans, it becomes quite difficult.
There are counter-strategies that females can employ to prevent infanticidal behavior from males. The previously mentioned Barbary macaque species is worth mentioning in this context. This species also lives in multi-male, multi-female groups yet lacks a polygamous mating strategy but one that is promiscuous. Females mate with all or most of the mature males in their group, which creates a condition of “confused paternity,” where any male in the troop is willing to help care for and protect all infants. The lack of infanticide can be seen as a benefit to female reproductive success. The extent of male investment is quite high even without certainty of paternity and one reproductive benefit for males in such a system is higher mating frequencies.
Apes
The Hominoidea group consists of tailless primates native to Africa and Southeast Asia within two separate branches: the “lesser” apes or gibbons and siamangs (family Hylobatidae, genera: Hylobates, Hoolock, Nomascus, and Symphalangus) and the “great” apes or hominids (orangutans, gorillas, chimpanzees/bonobos, and humans, or hominids/hominins). The terms lesser and greater are not holdovers from past hierarchical views of life where humans naturally occupied the top rung on the ladder and any animals less similar to us were more primitive or further down the evolutionary ladder. It is a reference to body size, since even the large siamangs are less than half the size of the smallest of the greater ape, the bonobo (Pan paniscus). Gibbons and siamangs are the true brachiators, with a far greater range of motion in their shoulders, while great apes, including humans, are modified brachiators, with this ability derived from an early common ancestor. The great apes were a key focus by anthropological researchers because of their genetic and evolutionary closeness to humans, especially for chimpanzees.
Several characteristics separate apes from the other primates considered previously. These include:
- Large brains, especially in the cerebral cortex associated with integration of sensory data.
- Long arms, short and broad trunks, no tails.
- Wrist, elbow, & shoulder joints allow a greater range of movement than in other primates.
- Hands are longer & stronger than other primates.
Ape long bone skeletal features reflect an evolutionary history that involved brachiation for a means of arboreal locomotion and of suspensory feeding. Old World monkeys move quadrupedally along tops of tree branches. Apes suspend themselves from below the branches and swing hand over hand through trees by forelimbs alone. This suspensory posture also translates to locomotion on the ground since all apes occasionally move bipedally on the ground and also in trees. The morphology and proportions of ape limbs depends on whether a species is adapted to living in the trees or to life on the ground: the arboreal apes include the gibbon and orangutan species that occupy dense tropical rain forests of SE Asia. Terrestrial or ground-dwelling apes consist of gorillas, chimpanzees/bonobos, and humans.
Ape dentition is also unique from that of monkeys with molars that are flat & rounded compared to monkeys and having a Y-5 cusp pattern on the lower molars (five cusps). Monkeys have a bilophodont pattern of four cusps & two ridges. This patterning allows paleontologists to readily distinguish ape from monkey teeth (at least molars) even when found in isolation from other remains. Surprisingly, this is one of the few ancestral conditions in apes, with bilophodont molars the derived feature in Old World monkeys while apes retain the Y-5 complex of earlier primates. All monkeys and apes have long canine teeth that project beyond the tops of the other teeth and a corresponding space in the opposite jaw called a diastema to accommodate the canines when the mouth is closed. Humans lack this feature, a marked distinction that appears millions of years ago in evolution of the human lineage. Given that large canines are used to help achieve reproduction success for males, the modification of this feature suggests that male-male competition was reduced in our lineage or other means of achieving dominance had evolved. Aside from reproductive aspects, the contact of the upper canine to the lower third premolar creates a sharp cutting edge (sectorial premolar).
Orangutans
Orangutans (genus Pongo) only live on the Indonesian islands of Borneo & Sumatra and consist of at least three species. They are the largest arboreal primates and subsist primarily on fruit (frugivores) with a fallback on a variety of other foods when fruit is not available. Because of overall low productivity of fruit in the forests, Orangutans live an essentially solitary life with hostility or avoidance occurring on encounters of the same sex. This solitary lifestyle and hostility to fellows disappears if resources are abundant, something that occurs at certain times in some places; all can observe such congeniality on display at zoos. Orangutans have the most pronounced sexual dimorphism of any apes, with males approximately two times larger than females on average. Males acquire and defend a territory from other males and females living within that defended territory preferentially mate with the resident male. Males provide no parental investment and females with infants appear to purposefully avoid males, likely out of a fear of infanticide. Wild orangutans generally spend little time out of the trees and on the ground but when they do their quadrupedal locomotion is different from and far less efficient than the knuckle-walking of gorillas and chimps/bonobos; it is more like walking on the sides of their fists and feet closed fist-like. Wild orangutans have been observed making and using tools for food extraction activities. Regional differences in the behavior suggest evidence for distinct orangutan cultures, just like among chimpanzees.
Gorillas
Gorillas, like chimps, are semi-quadrupedal knuckle-walkers but the similarities end there. The social and reproductive organization of gorillas is entirely different. Gorillas lack the complex social dynamics seen among chimpanzees, who live in much larger multi-male and multi-female groups and with a promiscuous mating strategy. Gorillas do not live in social groups capable of war (Inter-group violent conflict) as do chimps. Gorillas live in groups of up to about 30 individuals that mainly consist of a dominant male called a silverback, sometimes other adult males, adult females, and immature offspring.
Gorillas have a harem-based mating strategy where the alpha male maintains exclusive access to reproductive females and defends that access from other males in the group (usually juveniles) and those outside the group. Males upon reaching maturity usually leave their natal group to be by themselves or with a few other bachelor males, biding their time and hoping to become sufficiently large and dominant so that they might take over some existing harem or capture/attract females from other groups. Females also usually leave their natal group upon reaching maturity, which serves to limit inbreeding. Females lack an obvious physical sign that they are ready to mate, as with chimpanzees, and in most cases, it is the female gorilla who initiates the mating process when ready.
In most groups there is generally just one silverback male who controls the rest of the group members and determines what will be done daily, both where and when. Most of each day is taken up with eating since gorillas consume a rather low-quality vegetarian diet that requires a considerable volume of leaves, tree shoots, and fruits to get enough nutrition. Gorillas sleep on the bare ground or in ground nests made from non-food plant items. They lack predators except for leopards, and this is rare because of group living and silverback males. The greatest threat to their existence is humans, both poaching for the meat market and zoos and the destruction of their habitats. Dian Fossey, the first scientist to study gorillas in their native habitat, was hacked to death with a machete the day after Christmas in 1985, likely by the poachers who she had battled against for years.
Chimpanzees & Bonobos
For a long time, the bonobo were not officially designated as a separate species, but now they are: chimpanzees are Pan troglodytes and bonobos are Pan paniscus. The paniscus part of the bonobo’s biological name reflects its smaller size relative to the chimps: basically meaning the diminutive Pan. Although bonobos are just slightly shorter on average than chimps, their more slender bodies means that they weigh less: bonobo males weigh 100 pounds on average whereas chimp males weigh 132 pounds. You would be wise not to pick a fight with either one. You will hear myths of chimps (and bonobos) being super strong, but the most detailed scientific study so far found that chimp muscle produces just 1.35 times more dynamic force and power than human muscle.
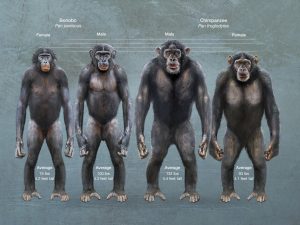
There are not only morphological and underlying genetic differences between these species, including some clear distinctions in aspects of brain anatomy, but some significant behavioral differences that largely stem from the distinct aspects of their computational hardware. In simplistic terms bonobos are the hippy chimp: they make love not war (and they make love in almost any way conceivable!). Chimpanzees make war (intercoalitional violence) with their neighbors, or at least what can be classified as a type of war: males from one community silently infiltrate the territory of a neighboring community seeking lone males and if this occurs then they attack viciously to kill that individual. Jane Goodall was the first to document such behavior and it shocked and unsettled her as documented in her memoir about chimp research. Bonobos do not engage in such violent encounters evidently because of poor cooperation among males within communities (gorillas and orangutans do not live in social groups capable of war). It is important to highlight that bonobos are aggressive, just slightly less so than chimps. Richard Wrangham, a well-known primatologist at Harvard, estimates that both species have displays of physical aggression more than 100 times frequently than humans do on average.
Both chimpanzees and bonobos have a combined terrestrial and arboreal adaptation, getting much of their food from the trees but also considerable ground resources, including items such as termites that they “fish” for with modified twigs. They were the first examples of tool use that Jane Goodall observed. They always retreat to the trees at night, building new nests each night just like orangutans. On the ground they are knuckle-walkers and can move rather fast this way over short distances. Both are excellent climbers and can move fast enough in the trees to catch monkeys, often the red colobus (genus Piliocolobus). A portion of both chimpanzee and bonobo diet comes from meat. Hunting alone or in small groups is an important activity for both chimpanzees and bonobos with chimps seeming to specialize in monkeys and bonobos hunting small antelope (duikers). Meat sharing is a common feature among chimpanzees although it is nothing like sharing seen among humans; it is basically a form of tolerated theft, although it is rather egalitarian in that low-rank chimps can also get a share.
Meat from hunting makes up a rather small part of their diet despite its social significance. Both chimpanzees and bonobos are omnivorous, which means they will eat almost anything, but prefer fruit and will focus on that if its available. Both species emphasize high-quality food items, those with great nutritional value, which is what fruit are, especially when ripe and sugar content is highest. Both species are quite choosy and consume ripe fruits almost all the time. Other high value items on the menu include eggs, caterpillars, ants and termites, honey, small invertebrates, flowers, leaf buds, seeds, tree resin, and of course meat from monkeys and other mammals. Both also eat leaves and stems or shrubs and trees, especially when young and the pith and bark.
Among the chimpanzee it is males that are the key instigators of hunting and the ones that usually have success and their communities are strongly patriarchal. Among bonobos it is females that commonly initiate hunting and their communities are strongly matriarchal, just like among many lemurs. With bonobos, a coalition of high-rank females dominate the majority of males and make the core of the group. With chimpanzees, it is a coalition of high-rank males, ones that are usually related, that make for the core of community groups. With chimps, males stay in their natal group and females disperse. This is a principal way that chimpanzee males build strong coalitions, by having genetically related males stay together. Male rank in the chimp social hierarchy is primarily based on physical displays of prowess that often involve aggression toward other group members. Male bonobos are less aggressive that chimp males and their status mainly comes from the status of their mothers; female bonobos are more aggressive than chimp females.
Chimpanzees and bonobos are less sexually dimorphic than all other great apes except for humans and both have a promiscuous reproductive strategy in their multi-male, multi-female social groups. Among chimps, dominant males tend to have greater access to females in estrus but they cannot exclude one another or even lesser rank males and females can sneak off for sexual encounters that sometimes include males of neighboring communities. Since males cannot control reproductive access to females and mating is promiscuous there is sperm competition and in both species males have the largest testicles compared to body size of the great apes (enhancing the quantity and quality of sperm). Gorillas with their harem-based reproductive strategy have the smallest testes relative to body size because they face no sperm competition; their male-male competition all occurs before insemination. Humans are intermediate between chimps/bonobos and gorillas in relative testis size, which some have argued implies that we descended from a lineage that followed a promiscuous mating strategy. However, research into sperm form and function indicates that humans are closer aligned to the low‐risk sperm competition of gorillas than to promiscuous chimp/bonobos. If so then the low degree of sexual dimorphism seen in humans, just slightly more than the monogamous gibbons, indicates little male-male competition in the form of overt physically violent contests.
Chimpanzees and bonobos have what is known as fission-fusion societies. What this means is that all members of a given community (territorial group) will rarely be together for all daily activities (feeding, grooming, etc.) or nightly activities (sleeping). There is a tendency for larger groups to sleep together, though rarely all members, but not to forage for food together. This breaking apart into smaller social groups is a huge benefit in allowing individuals to find sufficient resources to maintain themselves. The emphasis on high-quality food results in intense resource competition between individuals because most of the time food resources simply do not occur in great abundance and they tend to have a patchy distribution in space and time. The small daily groups can range from solitary animals to groups a few to several individuals and may consist of any combination of age and sex. There are obvious dangers in this from predators and also neighboring groups for chimps, but also benefits of having no or lessened resource competition and the social antagonism that comes with it.
Chimpanzees and bonobos make and use tools. Behaviors include termite fishing, leaves as napkins and for sponges, sticks as spears for hunting bush babies (galagos, nocturnal primates in the strepsirrhine group), various types of hammers and anvils to crack nuts, and more. Researchers point to differences in tool use among communities of chimpanzees providing evidence for chimpanzee culture, learning traditions that persist and that are variable across space. Chimpanzee tool use provides a useful comparative model in relation to human tool use by examining what features are shared in common and which are more human specific.
Primate Evolution
In order to understand our place in the evolution of our species, we need to look at the general evolutionary pattern of primates and a time frame that stretches back millions of years. Each major focus of primate evolution is divided by geological epochs.
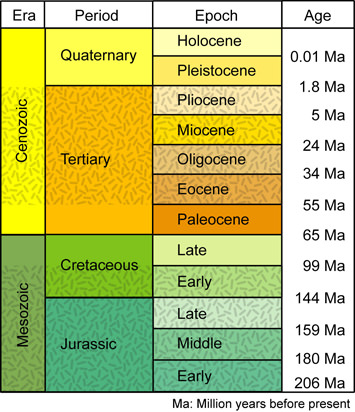
The Tertiary Period (65 million to 1.8 million years ago)
The Tertiary Period is the largest component of the Cenozoic Era, the so-called Age of Mammal. It is at the beginning of the Tertiary Period/Cenozoic Era that we begin to see creatures evolving that we classify as early mammals which have been the dominate animal in both southern and northern hemispheres of Earth. This expansion of mammals is believed to have followed a major planetary extinction event at the boundary of the Cenozoic/Paleogene Eras, caused by an asteroid impact. This extinction event allowed the expansion of early mammals as environmental niches opened up with fewer animal species on the planet. Each of the following epochs details aspects of primate evolution, primarily divided into 10 to 20 million year intervals.
Paleocene Epoch (65 to 55 million years ago)
The Paleocene is the first division of the Tertiary Period and is recognized as a major shift in planetary biological evolution, with the almost complete absence of reptilian species, including dinosaurs. With this niche almost completely absent, we see the expansion and proliferation of mammals with most characteristics of some species still present in our world today. These archaic forms or highly specialized mammals included opossum-like marsupials and herbivorous mammals that had teeth more akin to modern rodents.
During the Paleocene the mammals taht most likely gave rise to primates belonged to a group called Plesiadapiformes. Although plesiadapiforms are similar to modern primates in a number of characteristics of their skeleton, they were still of a much earlier evolutionary form, comparable perhaps to the living tree-shrews and not genuinely belonging to the order Primates.

Eocene Epoch (55 to 34 million years ago)
The first populations of primates evolved in tropical environments. While the first set is seen in the upper Eocene, primates continue to evolve throughout the later epochs, Oligocene and Miocene, as well. Early primates (also called euprimates) are found in fossil beds in North America (including Colorado and Wyoming) Europe, Asia, and possibly Africa. In many cases we identify living correlates to the extinct primates to help us predict their behaviors. Extant lemurs and lorises of Madagascar and Southeast Asia, respectively, are often used as approximations of primates from the extinct Family Adapidae, the first group of primates to evolve. Tarsiers are often predicted to be analogous to the second group of primates to evolve, Family Omomyidae. Both of these families represent massive radiations of primates throughout the world during the Eocene. Common themes of these primates include smaller body and brain sizes, probably nocturnal lifestyle, and locomotion via vertical clinging and leaping.
Physical features of the omomyids include large eye sockets (orbits), shortened noses (rostra) and consequent dental arcades, loss of premolars and an expansion of cheek teeth for the exploitation of insectivorous or frugivorous (fruit-eating) diets as well as a small body size of less than 500 grams (slightly more than a pound). Like many modern primates, these animals had grasping hands and feet with nails instead of claws. It is most likely these were tree-dwelling animals and perhaps leapers for some species with fused tibia and fibula (lower leg bones).

Oligocene Epoch (34 to 24 million years ago)
The Oligocene Epoch extends from about 34 to 24 million years ago within the Paleogene Period. During this epoch, the major continents continued to drift to their current positions and Antarctica became more isolated as it developed an ice cap. Mountain building began in western North America and the Alps began to rise in Europe as the African plate pushed northward into the Eurasian plate. With the expansion of the terrestrial landscape, animals, particularly mammals, began to expand in size.
Interestingly, in the previous Eocene Epoch we see an expansion of primate-like creatures throughout much of the northern hemisphere. However, it is early in the Oligocene epoch that we see monkey ancestors evolve with most of our evidence coming from Egypt! The most important sites for the Oligocene occur in Egypt, from the Fayum (al-Fayyum) region of the great Western Desert. It is there that we begin to see the earliest monkeys, about 30 million years old, that would eventually give rise to platyrrhines (New World monkeys with three premolars), including Proteopithecus, Parapithecus, Apidium, Oligopithecus, and Qatrania. But it isn’t until the end of the Oligocene Epoch, around 25 million, we begin to see the earliest platyrrhine fossils in South America. How did they get from Egypt to South America? The short answer is, we don’t know. There is no evidence of fossil primates in South America during that 5 million year span. The current prevailing theory is they rafted across the ocean on floating vegetation!
Continuing in the Oligocene and in Fayum, Egypt, monkeys evolve further and we can identify ancestors to modern catarrhines (Old World monkeys with two premolars), including Catopithecus, Propliopithecus, and Aegyptopithecus. Aegyptopithecus gave rise to the living catarrhines, both arboreal and terrestrial with no division until 29 to 24 million years ago. Thus, the Fayum appears to be the “cradle” of catarrhines and platyrrhines. From these primates in the Fayum, it appears that quadrapedalism (walking on all fours limbs) was the typical locomotion pattern and vertical clinging and leaping (as found in the earlier Eocene) was no longer retained by these animals.

The primate, Aeqyptopithecus zeuxis is an early catarrhine, as
discussed above, found primarily in the Fayum region of Egypt from the early Oligocene. It had a small body and long tail, quadrapedal with curved phalanges for an arboreal (tree-living) lifestyle, was likely a good leaper, and had a dental formula of 2:1:2:3, thus, a descendent of catarrhine primates with the same dental formula. The dental wear of this species suggests they were frugivorous, but could occasionally eat hard objects. The canines of these individuals were sexually dimorphic, with the males have larger canines than the females along with a more developed sagittal crest (ridge of bone along the anterior/posterior cranium) in males.
Miocene Epoch (24 million to 5 million years ago)
The expansion of primates seems to explode during the Miocene Epoch, 24 to 5 million years ago. This is an extremely dynamic period during the Earth’s morphology, with volcanism and mountain building. Much of the modern world’s topography occurred during this time period. With the creation of various mountain chains we see changes in vegetation; the vastly forested regions that start the epoch start to shrink and the creation of grasslands or savannas occurs. With the expansion of grasslands (savannas, llanos, and prairies), we begin to see the first ground-dwelling primates with their generalized body type and expansion of the brain.
Important areas of research include East Africa and Central Europe, primarily with complete skeletons of the group, Proconsul (Family Pronsolidae). Reconstructions of Proconsul indicate that it is very similar in body size and morphology (shape) of modern Old World monkeys but is more ape-like in its form. Since the 1980s, this family of proconsuls has expanded tremendously with numerous new genera identified. We won’t go over these here, but there was an expansion of this form of primate during the Miocene period!
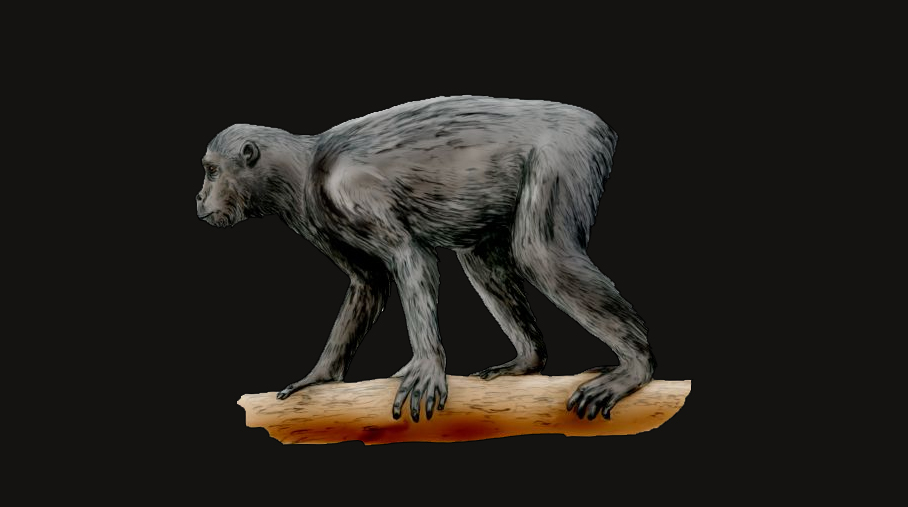

Pliopithecidae became widespread in Europe with its best-known genus, Pliopithecus, found in the modern Czech Republic. These creatures were a tailed quadraped that retained numerous physical characteristics of extant monkeys. Pliopithecines are considered to have diverged from primitive catarrhines, probably before Pronconsulidae became a separate family.
Dryopithecus sp. were a fossil ape found in western Europe, including Spain, France, and Hungary. They are truly an unknown quantity as there is no evidence they moved out of Europe (i.e., went extinct as forests disappeared) and no fossils in Africa to identify the descendents of modern apes there. In the Siwalik Hills of Pakistan and northern India, during the Middle to Late Miocene, there was Sivapitehcus, a potential ancestor to the living orangutans. Finally, during the Late Miocene, we find Oreopithecus, the so-called Abominable Coal-man (originally specimens were found in an Italian lignite/coal mine).
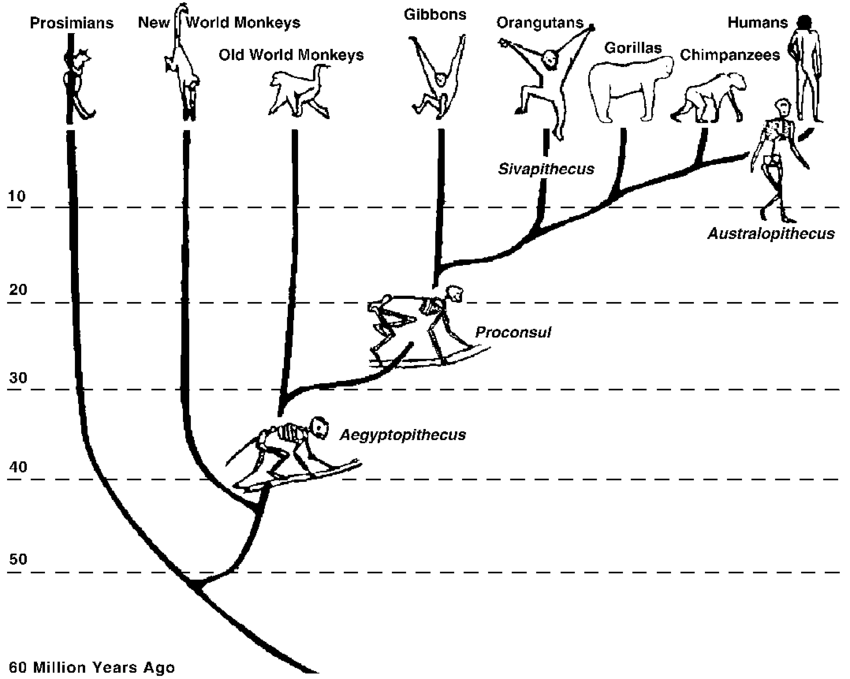
Oreopithecus possesses a number of dental and skeletal characteristics of hominids, particularly short canines and a reduced snout (subsequently with a smaller face). This species also shows a lot of charactersitics of a ‘transitional’ form with characteristics of a brachiator (swinging from trees), such as long arms and long, curved fingers. It has also been suggested their pelvic girdle showed features associated with bipedal walking, though it is most likely that Oreopithecus is an evolutionary deadend and not part of human’s direct ancestry.
With these beginnings of hominid evolution, the branches continue after the Miocene. Both gorillas and chimpanzees have evolved over the years and are not representative of the last common ancestor with humans. To make tracing our evolutionary history even more complicated, there is a gaping hole in the fossil record for African apes, with very few species known to science. Without this information, we can only make assumptions about how apes, and subsequently humans, would have evolved. What we do know though is that over the last 7-10 million years, we see an expansion of the order primates to include more and more human-like (bipedal) creatures.
The scientific study of primates both living and extinct by conducting both field (in the wild and in zoos) and laboratory research so as to understand aspects of their evolution, anatomy, and behavior.
This term describes a shift in the function of a trait during the course of evolution. A trait that evolved because it served one particular function, may subsequently come to serve another function. This occurs in both anatomy and behavior, including human culture.
This refers to behaviors involved in cleaning and maintaining body function and hygiene. In primates it is commonly a major social activity (also termed allogrooming) that helps animals living in close proximity to bond and reinforce social structures, family links, and build companionships. It is used in conflict resolution in some species.
The ability to see things in three dimensions (3-D). Stereoscopic vision is what allows for true depth perception.
Being awake and active during the daylight hours but sleeping during the nighttime. Humans like all apes and most monkeys are diurnal.
Being awake and active when it is dark but sleeping during the day. This trait was likely characteristic of most or all early primates but in now only retained in prosimians.
A moist, hairless pad of skin at the end of a nose. This is a characteristic of most mammals including dogs and cats. This feature is absent in primates except for prosimians (exclusive of tarsiers).
The naming, describing, and classifying organisms into different categories on the basis of their appearance and other diagnostic characteristics as well as their evolutionary relationships. The biological sciences primarily use the Linnaean classification system for this purpose. Classification was originally based on morphology but now DNA barcoding is the gold standard (see https://ibol.org/about/dna-barcoding/).
Teferring to animals that spend most of their time on the ground rather than in the air, water, or trees. Most ground dwelling primates retreat to trees or other safe places such as rock outcrops to sleep at night.
the ability to physically grasp something. All primates have prehensile hands. With the exception of humans, they all also have effective prehensile feet. The larger New World monkeys (Atelidae) have prehensile tails with sensitive, almost hairless, tactile pads on the underside distal part.
Refers to anatomical differences between males and females of the same species. Primate males are usually significantly larger and more muscular than females. This is especially true of semi-terrestrial monkeys and the great apes. Humans are also sexually dimorphic.
A single adult male defends a group of females from other males and, while his tenure lasts, enjoys exclusive mating access to those females. This is sometimes referred to as a harem‐based mating system. Primates with this pattern live often live in one-male multi-female groups, and the females tend to be related since they stay in their natal group (philopatric) and males move out upon reaching sexual maturity.
Both males and females mate with multiple members of the opposite sex and live in multi-male multi-female groups. Another term for this pattern is promiscuous.
The dependent variable is the factor that is influenced in some way by an independent variable.
The independent variable is the one that is assumed to have a direct effect on some other factor(s) called the dependent variable(s).
A bone structure or organ of an organism whose function seems to have lost all or most of its original purpose in a given species.
The independent evolution of features similar in form or function in two species with different ancestral origins, with the features not present in the last common ancestor of those groups. This occurs because lifeforms often develop similar solutions to the same kind of problems presented by occupying similar habitats.
A form of dyadic relationship in which an individual has only one sexual partner for some interval of time such as a breading season or lifetime. Serial monogamy involves a succession of monogamous sexual relationships.
A form of polygamy in which a female mates with two or more males at the same time. This is quite rare among humans, but when it occurs the males are commonly brothers.
Behaviors that increase the fitness of offspring during their pre-reproductive age; behaviors such as feeding or carrying infants, grooming and playing with young offspring (direct investments) and other behaviors such as defense of territory or females and elimination of competitors (indirect investments).
A member of the same species.
A mode of natural selection that occurs in two distinct ways: (1) intersexual selection whereby members of one biological sex choose mates of the other sex to mate with (often female choice), and (2) intrasexual selection whereby members of the same sex compete, often ferociously, for access to members of the opposite sex (often males). Both forms of selection mean that some males have greater reproductive success than others either because they are more "attractive" for one type of fitness display or another or because they have won out against rival males in dominance contests.
A space separating teeth of different functions. For primates especially, it is the gap between the incisors (biting teeth) and premolars and molars (grinding teeth) that accommodates large canines. Humans lack this feature.
An animal that eats plant foliage, with young leaves and stems preferred by those primates with this herbivore pattern. Immature vegetation is easier to chew with less hard-to-digest cellulose, tends to be more nutritious (higher energy and protein), and contain less toxic compounds. Since leaves are an abundant resource of low value there is little or no resource competition between individuals.
A form of arboreal locomotion in which primates swing from tree limb to tree limb using only their arms.
The interval when females are sexually receptive as controlled by specific hormones and often accompanied by changes in behavior and physiology that signal their receptive condition. In many primates these physiologic changes consist of highly visible swelling and reddening of the genital and perineal skin. Humans female lack this trait and are characterized by hidden estrus or cryptic ovulation.
Sperm competition theory argues that the number of sperm inseminated into a female is a trade-off between two opposing pressures: (1) sperm in competition with the sperm of other males favors the male inseminating more sperm; (2) yet ejaculates are costly to produce and males should economize the number of sperm inseminated.
This basically means that food resources are not distributed uniformly in the environment (resources are not homogeneously distributed) but tend to occur clustered in specific places (patches). Moreover these patches might have a temporal component (seasonality of occurrence) in addition to the spatial component.
A geological epoch is a time period that is a subdivision of a geological period. For example, we are currently in the Quaternary Period of the Holocene Epoch (although some researchers have suggested that we are in a new epoch, the Anthropocene, that reflects humanity's influence on the environment of our planet).
A geological period is major subdivision of geological time based on events as interpreted in rocks and stratigraphy. Each period is a sub-division of an era.
A geologic era is a subdivision of geologic time that divides an eon into smaller units of time.
early forms
Marsupials are a group of animals whose members are thought of as pouched animals and whose young ones are born partly developed instead of internally in a womb.

