25
Vitamins and Minerals
There are a total of 13 essential vitamins, eight of which belong to the B-group. These vitamins and minerals play crucial roles in supporting the body’s functions, including boosting the immune system, promoting wound healing, increasing bone strength, and regulating hormonal balance.
Vitamins and minerals, often referred to as “micronutrients,” are essential nutrients that we obtain from our food. These micronutrients play a crucial role in our metabolic processes, assisting our bodies in extracting energy from macronutrients, which include carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
Vitamins
Vitamin A
 Function:
Function:
- enhances immune system to protect against diseases and infections
- maintains healthy skin
- assists reproduction and development
- eye health
Where to find it:
- Yellow and orange fruits and vegetables
- apricots, carrots, cantaloupe, mangoes, sweet potatoes, pumpkin
- Leafy greens
- broccoli, spinach, peas
- Eggs, liver, milk
Vitamin B
| Thiamin (B1) | Riboflavin (B2) | Niacin (B3) | Pantothenic Acid (B5) |
| Pyridoxine (B6) | Biotin (B7) | Folate or Folic Acid (B9) | Cyanocobalamin (B12) |
 Function:
Function:
B vitamins play a crucial role in helping the body utilize energy from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. It’s important to note that most B vitamins cannot be stored in the body, with the exceptions being B-12 and folate. To ensure sufficient intake of these essential vitamins, it’s important to include them consistently in your diet.
Where to find it:
- fish
- fruit
- lean meats
- vegetables
- whole grains
Vitamin C
 Function:
Function:
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, plays a vital role in various metabolic functions in the body. Unlike some nutrients, the human body cannot synthesize vitamin C from other compounds, making it essential to obtain through dietary sources. Furthermore, because vitamin C cannot be stored in the body for extended periods, it is important to include it in our daily diet to maintain optimal health.
- Essential antioxidant, plays a crucial role in eliminating free radicals produced during oxygen metabolism in the body. These free radicals can potentially disrupt cellular function, making the antioxidant vital for maintaining overall cellular health.
- Collagen production for skin, blood vessel, and bone health, as well as wound healing
- Assists in iron intake
- Support lymphocytes in immune function
- Development of brain neurotransmitters
Where to find it:
- Fruits
- kiwi, lemons, limes, mangoes, oranges, strawberries, tomatoes
- Vegetables
- broccoli, brussel sprouts, cabbage, cauliflower, potatoes
Vitamin D
 Function:
Function:
The maintenance of healthy bones and muscles relies on several factors, one of which is vitamin D. Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun plays a crucial role in the synthesis of vitamin D within the skin. Additionally, engaging in consistent physical activity further supports the body’s ability to produce this vital nutrient.
Where to find it:
- eggs
- fatty fish (salmon)
- milk
Vitamin E
 Function:
Function:
Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that plays a crucial role in supporting the body from disruption caused by free radicals. These free radicals can arise from various sources, including exposure to smoke and radiation, leading to oxidative stress and potential harm to cells. By neutralizing these harmful compounds, vitamin E helps maintain overall health and supports the body’s defense mechanisms.
- immunity
- skin
- vision
Where to find it:
- egg yolks
- leafy greens
- broccoli, spinach
- meat
- liver
- nuts and seeds
- almonds, hazelnuts, peanuts, sunflower seeds
- oils
- extra virgin, sunflower, soybean
- unprocessed whole grains
- wheat germ
Vitamin K
 Function:
Function:
Vitamin K plays a crucial role in maintaining strong bones, promoting effective blood clotting, and facilitating the wound healing process. Vitamin K is an essential nutrient that can be obtained from various foods as well as produced by beneficial bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract. However, newborn babies are born with very low levels of this vitamin and lack the necessary gut bacteria to synthesize it. To address this deficiency, newborns typically receive a booster shot of Vitamin K shortly after birth, helping to elevate their Vitamin K levels and support their health.
Where to find it:
- fruits
- avocado, kiwi
- leafy greens
- kale, spinach
- vegetable oils
- soybean oil
Minerals
Calcium
 Function:
Function:
Calcium plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy bones. Insufficient calcium intake can lead to osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones.
- blood clotting
- enzymes
- muscle and heart health
- nervous system function
- promote healthy bones and teeth
Where to find it:
- dairy products
- cheese, milk, yogurt
- nuts
- almonds
- vegetables
- broccoli, bok choy, kale, watercress
Iodine
 Function:
Function:
Iodine plays a crucial role in the production of thyroid hormones, which are essential for regulating metabolism. Additionally, these hormones support healthy development of both the brain and the body.
Where to find it:
- dairy products
- eggs
- seafood
- seaweed
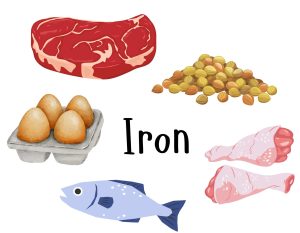
Iron
 Function:
Function:
Iron is a crucial mineral that plays a vital role in transporting oxygen throughout the blood. Additionally, it supports the immune system in its efforts to combat infections.
Where to find it:
- eggs
- fish
- legumes
- poultry
- red meat
Magnesium
 Function:
Function:
Magnesium plays a vital role in various bodily functions. It contributes to the development and maintenance of strong bones, facilitates the conversion of glucose into energy, and supports immune system function. Additionally, magnesium is important for managing blood pressure and promoting lung health.
Where to find it:
- chocolate and cocoa
- dark green vegetables
- legumes
- nuts
- cashews
- seafood
- whole grains
Potassium
 Function:
Function:
Potassium plays an essential role in the proper functioning of nerves, muscles, and the heart. Additionally, it is beneficial in helping to lower blood pressure, making it a vital nutrient for overall health. Consuming unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and lean meats, offers numerous health benefits. In contrast, highly processed foods that are high in salt can lead to a decrease in potassium levels in our bodies.
Where to find it:
- fruits
- apricots, bananas
- nuts and seeds
- vegetables
- mushrooms, spinach
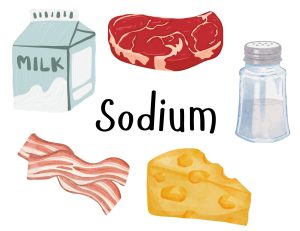
Sodium
 Function:
Function:
Sodium plays a vital role in optimizing good health, as it helps regulate the volume of circulating blood and tissue fluids in the body. However, many individuals consume excessive amounts of salt, which can lead to health issues such as high blood pressure and other related complications. It is important to balance sodium intake to support overall well-being.
Where to find it:
- salt
- dairy products
- meat
- whole grains
Zinc
 Function: Zinc is a vital mineral that plays a crucial role in supporting the immune system as well as promoting growth and development. It is instrumental in the production and absorption of vitamin A within the body.
Function: Zinc is a vital mineral that plays a crucial role in supporting the immune system as well as promoting growth and development. It is instrumental in the production and absorption of vitamin A within the body.
Where to find it:
- dairy products
- cheese, milk
- poultry
- red meat
- shellfish
- whole grains
Risk of vitamin and mineral deficiencies:
- dieting
- elderly
- food allergies
- malabsorption difficulties (celiac disease, cystic fibrosis, diarrhea, pancreatitis)
- pregnancy, breastfeeding
- smoking
- vegetarians, vegans
- women with heavy menstruation
References:
Victoria State Government. (2024, July 24). Vitamins and minerals. Better Health Channel. https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/healthyliving/Vitamins-and-minerals
Media Attributions
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin B
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin K
- Calcium
- Iodine
- Iron
- Magnesium
- Potassium
- Sodium
- Zinc
