Life Drawing
“I have always liked drawing, when you draw you see things more intensely.”
Henry Moore

Standing Figure. 1848/52. Jean François Millet. Public Domain. Courtesy of the Art Institute of Chicago.
Life Drawing: A Helpful Guide, by Mahara Sinclaire, Assistant Professor, Pasadena City College. CC BY NC 4.0.
What Gesture Drawing Is YouTube
Figure Drawing Fundamentals YouTube
Life drawing helpful guide: OER (Open Educational Resources)
Introduction to Human Anatomy for Artists Proko YouTube
Drawing from human models: Line of Action
Robert Beverly Hale Lectures YouTube
Human Body Proportions – Anatomy Master Class YouTube
Drawing Life YouTube
How to Combine Gesture and Anatomy Proko YouTube
Combining Gesture and Anatomy Step by Step Proko YouTube
VOCABULARY
ABSTRACT SHAPE: a shape derived from a visual source but is so transformed that it bears little resemblance to the referent.
ACTUAL SHAPE: a positive area with clearly defined boundaries (as opposed to an implied shape).
AESTHETICS: sensitive to beauty or art
AMORPHOUS SHAPE: a shape without clear definition: formless, indistinct, and of uncertain dimension.
ANALOGOUS COLORS: colors that are closely related in hue. They are usually adjacent to each other on the color wheel.
ASYMMETRY: “without symmetry” having unequal or noncorresponding parts.

Anatomical Study and Sketch of Kneeling Figure, pen and ink on paper, Follower of Michelangelo Buonarroti. n.d. CC0
BALANCE: a sense of equilibrium between areas of implied weight, attention, attraction, or moments of force.
BIOMORPHIC SHAPE: an irregular shape that resembles the freely developed curves found in living organisms.
BLIND CONTOUR: drawing the contour of a subject without looking at the paper.
CALLIGRAPHIC: elegant, flowing lines made with a special pen or ink. An expressive quality seen in calligraphy. Lines that are flowing and rhythmical, like the qualities found in calligraphy.
CHIAROSCURO: 1. distribution of light and dark in a picture 2. a technique of representation that blends light and shade gradually to create the illusion of three-dimensional objects in space and atmosphere.
COMPLEMENTARY COLORS: two colors, equally spaced on the color wheel, directly opposite each other on the color wheel.
COMPOSITION: the arrangement and/or structuring of all the art elements, according to the principles of organization, that achieves a unified whole. Often used interchangeably with the term design.
CONE OF VISION: in perspective drawing, a hypothetical cone of perception originating at the eye of the artist and expanding outward to include whatever he or she wished to record in an illusionistic image such as a perspective drawing. The cone’s maximum scoping angle is 45 to 60 degrees; anything outside of the cone of vision is subject to distortion.

CONTENT: the expression, essential meaning, significance, or aesthetic value of a work of art. Content refers to the sensory, subjective, psychological, or emotional properties we feel in a work of art, as opposed to our perception of its descriptive aspects alone.
CONTOUR LINE: the line that defines the outermost limits of an object or a drawn shape. Sometimes considered to be synonymous with outline.
CROSS CONTOUR LINE: a line that moves across a shape or object to define the surface undulations between the outermost edges.
CROSSHATCHING: lines passing over hatching lines in a different direction, usually resulting in darker values.
CUBISM: an approach invented around 1907/1908 by artists Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque. They presented different views of objects and figures together in the same image, resulting in paintings that look fragmented and abstract.
CURVILINEAR SHAPE: a shape whose boundaries consist of curved lines; the opposite of rectilinear.

DADAISM: the earliest style of Fantastic Art to appear in the 1900s that opened modern art to a new freedom of humorous expression, creative imagination, contradictory tendencies, and intentional provocation.
EXQUISITE CORPSE: producing visual artwork devised by the Surrealists in which several people collaborate in creating an image.
FIGURE: the primary or positive shape in a design; a shape that is noticeably separated from the background. The figure is dominant, advancing shape in a figure-ground relationship.
FIGURE/GROUND REVERSAL: an arrangement in which the positive and negative shapes alternately command attention. Also known as positive negative interchange.
FOCAL POINT: the point of emphasis in a design or picture, which attracts attention and encourages the viewer to look further.
FORESHORTENING: a term that applies to organic and anatomical forms seen in radical perspective, as in the portrayal of lines being shorter than they are, to create the illusion of correct size-and-shape relationships in space.

FORM: the total appearance, organization, or inventive arrangement of all the visual elements according to the principles that will develop unity in the artwork; composition.
FORMAT: the type of picture frame used for the outer edge of a design (landscape/ portrait).
GENRE: paintings/drawings with subject matters that concern everyday life, domestic scenes, family relationships, and the like.
GEOMETRIC SHAPE: a shape that appears related to geometry usually simple, such as a triangle, rectangle, or circle.
GESTALT: a German word for form. Our reaction to the whole is greater than our reaction to its individual parts or characteristics, and our minds integrate and organize chaotic stimuli so that we see complete patterns and recognizable shapes.
GESTURE: lines that are drawn freely, quickly, and seemingly without inhibition to capture the intrinsic spirit of an animation seen in the subject. Gestural lines can imply the past, present, and future motion of the subject.
GROUND: the negative shape or background design.

HATCHING: a repeated stroke of an art tool, producing clustered usually parallel lines that create value.
HUE: the generic name of a color; also designates a color’s position in the spectrum or on the color wheel. Hue is determined by the specific wavelength of the color in a ray of light.
IMPLIED SHAPE: a shape that does not physically exist but is suggested through the psychological connection of dots, lines, areas, or their edges.
LINE: a path of a moving point made by a tool, instrument, or medium as it moves across and area. A line is usually made visible because it contrasts in value with its surroundings. Three-dimensional lines may be made using string, wire, tubes, solid rods, and the like.
13 Types of Line YouTube
LINEAR PERSPECTIVE: a system used to depict three dimensional images on a two-dimensional surface; it develops the optical phenomenon of diminishing size by treating edges as converging parallel lines that extend to a vanishing point or points on the horizon (eye level) and recede from the viewer.
MASS GESTURE: rendering the solidity of a subject by bold tone or color, without emphasis on lines or edges. Also known as weight and modeled drawings. A basic exercise in figure drawing, like gesture drawing.
MONOCHROMATIC: having only one hue; may include the complete range of value (of one hue) from white to black.
NEGATIVE SHAPE: a clearly defined area around a positive shape; the receding shape or ground area in a figure-ground relationship. A shape created through the absence of an object rather than through its presence.

ORGANIC SHAPE: a shape commonly found in nature.
PICTURE FRAME: the outermost limits or boundary of the picture plane.
PICTURE PLANE: the actual flat surface on which the artist executes a pictorial image. In some cases, the picture plane acts merely as a transparent plane of reference to establish the illusion of forms existing in a three-dimensional space.
PLANAR: an analysis of complex curved surfaces into flat planes by using straight lines and geometric shapes. This process helps understand the underlying structure of objects that results in a mechanical appearance.
POSITIVE SHAPE: the principle or foreground shape in a design; the dominant shape or figure in a figure-ground relationship.
PRIMARY COLOR: a preliminary hue that cannot be broken down or reduced into component colors. Primary colors are the basic hues of any color system that in theory may be used to mix all other colors.
PROPORTION: the comparative relationship of size between units or the parts of a whole. For example, the size of the Statue of Liberty’s hand relates to the size of her head.
PURE FORM: a non-objective shape created without any reference to a specific subject matter.
RECTILINEAR SHAPE: a shape whose boundaries consist of straight lines; the opposite of curvilinear.

SCRIBBLE: creating work quickly and loosely, scribble lines give way to form and shape. A method that uses random, uncontrolled lines.
SECONDARY COLOR: a color produced by a mixture of two primary colors.
SHADE (of color): a color produced by mixing black with a hue, which lowers the value level and decreases the quantity of light reflected.
SHAPE: an area that stands out from its surroundings because of a defined or implied boundary or because of differences of value, color, or texture.
SPLIT COMPLEMENT: a color and the two colors on either side of its complement.
SUBJECT: 1. in a descriptive approach to art, refers to the persons or things represented. 2. in more abstract applications, refers to visual images that may have little to do with anything experienced in the natural environment.
SUBTRACTIVE COLOR: the sensation of color that is produced when wavelengths of light are reflected to the viewer after all other wavelengths have been subtracted and or absorbed.
SURREALISM: a style of artistic expression, influenced by Freudian psychology, that emphasizes fantasy and whose subjects are usually experiences revealed by the subconscious mind through the use of automatic techniques (rubbings, doodles, blots, cloud patterns, etc.) originally a literary movement that grew out of Dadaism, Surrealism was established by a literary manifesto by André Breton in 1924.
SYMMETRY: the exact duplication of appearances in mirror like repetition on either side of a straight-lined central axis.

TEMPERATURE: the physical and psychological heat generated by a color.
TERTIARY COLOR: color resulting from the mixture of all three primaries, two secondary colors, or complementary intermediates. Tertiary colors are characterized by the neutralization of intensity and hue.
TETRAD (of color): four colors, equally spaced on the color wheel, containing a primary and its complement and a complementary pair of intermediates. This has also come to mean any organization of color on the wheel forming a rectangle that could include a double split complement.
TINT: a color produced by mixing white with a hue, which raises the value level and increases the quality of light reflected.
TRIAD: three colors that are equidistant on a color wheel.
TROMPE L’OEIL: a French term meaning, “to fool the eye.” The copying of nature with such exactitude as to be mistaken for the real thing.
VALUE: 1. The relative degree of lightness or darkness. 2. The characteristic of color is determined by its lightness or darkness, or the quantity of light reflected by the color.
VANISHING POINT: in linear perspective, the point, or points on the eye level at which parallel lines appear to converge.
Videos focusing on media, approach, and technique:
Charcoal/ Portraits
Quick Portrait Sketch in Charcoal YouTube
5 Minute Charcoal Portrait Tutorial YouTube
Charcoal Portrait from Life YouTube
Scribble approach
How to do Scribbling Art YouTube
Realistic Skull YouTube
Chaotic Line YouTube
Gesture
How to See the Gesture YouTube
Gesture Do’s and Don’ts YouTube
Clothing
How to Draw Clothing on Dynamic Figures YouTube
How to Draw a Body (Clothed) YouTube
Charcoal Fabric YouTube
Cross contour
Cross Contour Lines Exercise YouTube
Cross Hatching
Drawing in Pen and Ink YouTube
Mini Lesson: Crosshatching in Pen YouTube
Foreshortening
Foreshortening with the Coil Technique YouTube
Draw People in Perspective Alphonso Dunn YouTube
Hands and feet
How to Draw Feet YouTube
How to Draw Feet Proko YouTube
How to Draw Hands David Finch YouTube
Drawing Hands YouTube
Hatching
Cross Contour Hatching Technique YouTube
Hatching Tutorial YouTube
Mass gesture
Mass Gesture YouTube
Planar
Boxes and Cylinders YouTube
Positive and negative
Draw Using Negative Space YouTube

Reverse or Reductive/Subtractive charcoal
Tutorial YouTube
Unusual figures
Hieronymus Bosch YouTube
Remedios Varo YouTube
Zdzistaw Beksiñski YouTube

Toned paper
Step by Step YouTube
How to Draw on Toned Paper YouTube
Sketchbook:
Fabric and figure study: Ask a roommate or friend to sit for you while you draw them in an outfit or wrapped in a blanket. Notice the peaks and valleys of the fabric, pay attention to where the shadows grow in and/or away from creases. Your light source will dictate the intensity of your value, your fabric material will define your texture quality. Study the examples below, color and pattern can be useful when mapping out surface areas.
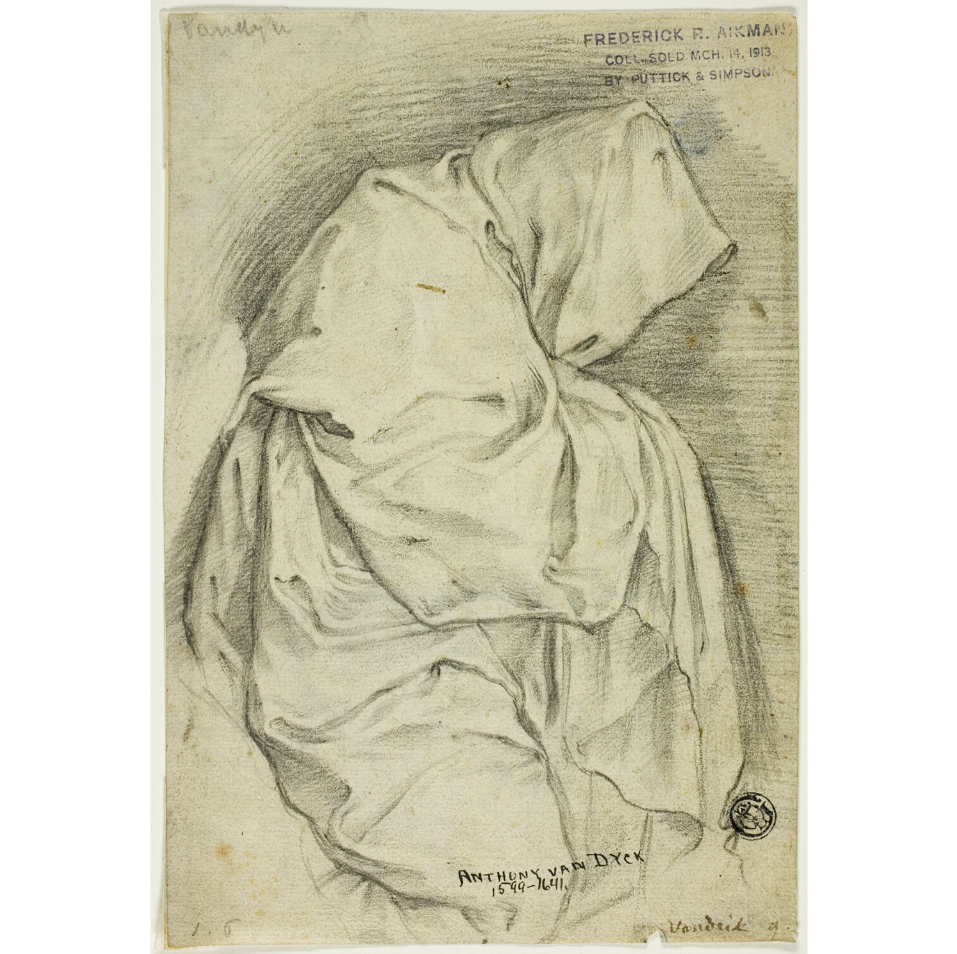


Cubist figure drawing or portrait: Use photo references or have a couple models pose for you while you initiate a Cubist style figure drawing. Study and draw your figure from multiple views to achieve a cubist like quality in your drawing. Rely on geometric shapes and angles to establish the forms and utilize color as a tool to emphasize the flat qualities that tend to appear in Cubist works.
Picasso’s Three Musicians at the MoMa YouTube
Half photo half graphite: Find a portrait in a magazine or from the internet (and print it off). Rip or cut it in half and draw the half you removed in pencil.
Process YouTube

Metaphor Drawing: Make a series of drawings based off a few of these sayings. What do these body parts look like without context or explanation?
Laced fingers
Crossed fingers
Twiddle thumbs
Locked knees
Braided hair
‘the’ finger
tuck your chin
roll your ankle
shin splint
pierced ears
forehead
kneecap
twirl your hair
worry lines
crow’s feet
thumbs up
lift your heals
Leg lifts
twist your arm
middle finger
pointer finger
ring finger
pinky finger
piggy toes
shoulder blade
Collar bone
lazy eye
kink in your neck
turned up nose
Charlie horse
Leg cramp
Furrowed brow
Cracked knuckles
Funny bone
Roll your eyes
Don’t let the door hit cha in the arse
Pain in the neck
Locked jaw
Sharp tongue
Cracking bones
Flick of the wrist
Pull your ear
Pull your leg
Achilles tendon
Wrapped around your finger
Skin and bones
Third eye
Belly button
Tippy toes
Bat your eyelashes
Tap your foot
Stomp your feet
Clap your hands
Grind your teeth
Reading:
Kenneth Clark: The Nude. A Study of Ideal Art jstor
John Berger: Ways of Seeing Chapter One
John Berger: Ways of Seeing Episode 1 YouTube
Writing:

The Storyteller’s Story: This ceramic figure was created in the Ameca Valley of Mexico. The figure appears to be in the midst of telling a story, and in many early societies storytellers told heroic legends and myths that helped people understand their history and their place in the natural world.
Though seated, its pose is energetic and its gestures expressive. Notice that the mouth on the Storyteller Figure is partially open. What does its posture tell you, the pose overall? Is the figure speaking? If so, what is he saying? Write the story Storyteller Figure might be telling.
Large projects:
Toned paper drawing: Make a full figure drawing in pastel, oil or dry. Proportions and measurements are crucial, work slowly to find accuracy. The entire figure needs to fill the composition, they may be nude or clothed (no padding like football or hockey players).
Skully Selfie: Start by drawing half of a human skull then add your face to opposite side of the skull.
Halloween Skull Face – Photoshop Tutorial
Artists to research:
Hayv Kahraman
Henry Moore
TATE YouTube
Henry Taylor
Philip Pearlstein
Lucian Freud
Jenny Saville
Iona Rozeal Brown
Mickalene Thomas
Wanda Ewing
Kehinde Wiley
Robert Gober
Alice Neel
Ellen Gallagher
Auguste Rodin
Advice for models: Open Figure Drawing
Human Figure Proportions: Cranial Units Proko YouTube
New Masters Academy: Timed Figure Poses 14 video series YouTube
Measuring the Figure in Life Drawing Otis College of Art and Design YouTube
How to Draw the Head from Any Angle Proko YouTube
Love Life Drawing YouTube
Bones: a mineralized connective tissue that exhibits four types of cells: osteoblasts, bone lining cells, osteocytes, and osteoclasts. The bone exerts essential functions in the body, such as locomotion, support and protection for soft tissues, storage of phosphate and calcium, and houses bone marrow.
Muscles: a tissue primarily composed of specialized fibers that contract and expand to effect movement.
Tendons: flexible but non elastic cord of strong fibrous collagen tissue that attaches muscle to bone.
Ligament: short band of strong, flexible fibrous tissue that connects two bones or cartilage together at a joint.
Fascia: a thin casing of connective tissue that surrounds and holds every organ, blood vessel, bone, nerve fiber and muscle in place. It provides internal structure and is as sensitive as skin.

