Two Dimensional Drawing
Defining Media, Tricks, and Tools: how it has been made, how it is used, and what it looks like.
Two Dimensional Drawing
Charcoal – charcoal is one of the first drawing materials used by man and was found in cave paintings from as far back as 27,000 years ago. To make charcoal, tree twigs and willow vines are heated at a hot temperature in an enclosed pit or oven type vessel where oxygen cannot get in. Depending on the substance, the charcoal material can be hard or soft. Charcoal 101, all about charcoal drawing
Everything I know about charcoal drawing in one video
6 of the best art techniques using charcoal
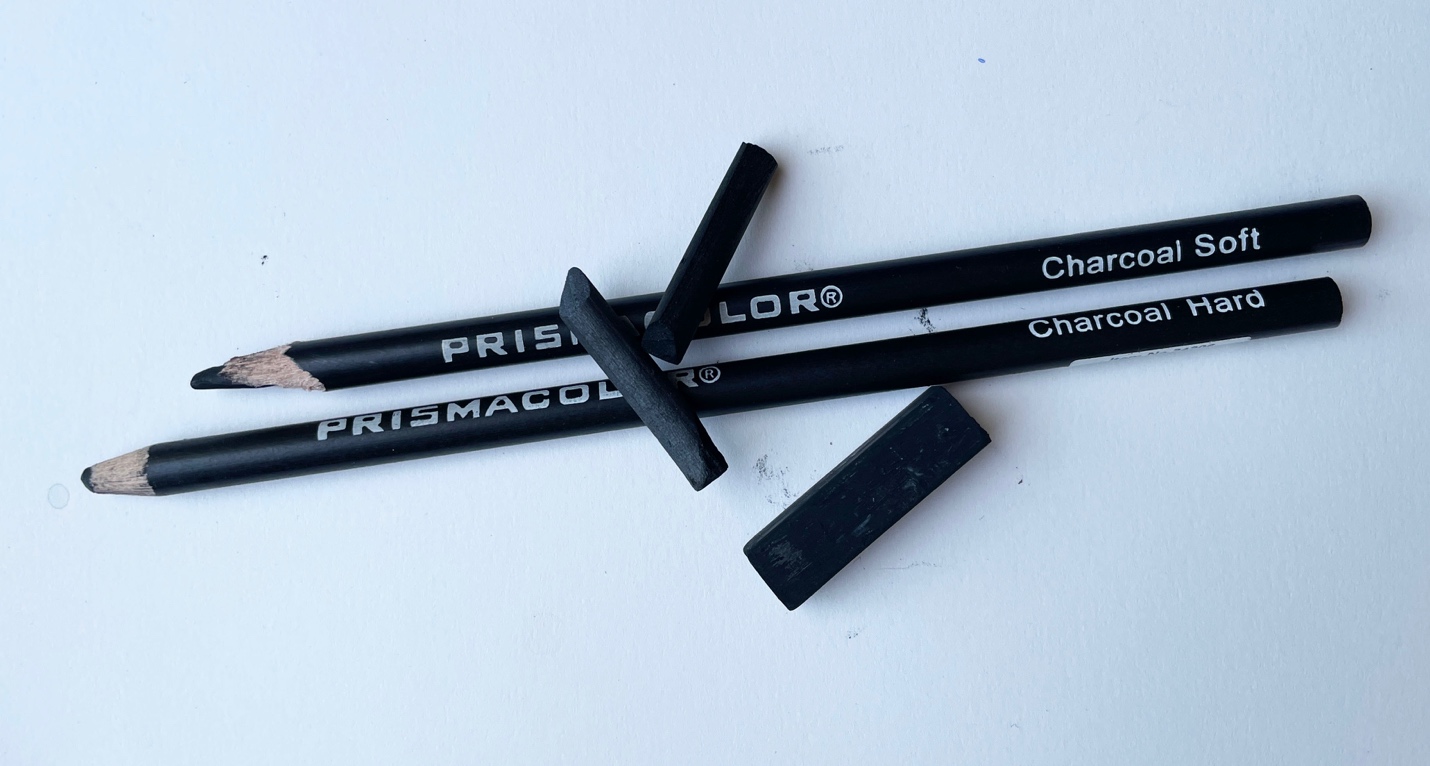

ahaney CC BY-SA 3.0
Conté – a French scientist Nicholas Jacques Conté invented conté crayon in the 18th century. It is a drawing material that is made from a mixture of graphite and clay. Traditionally, it has been produced in black, brown, and sanguine (red). Nowadays you can find it in any color. Conté a can be formed into a crayon or embedded into a pencil format. Conte Crayon drawing Demo
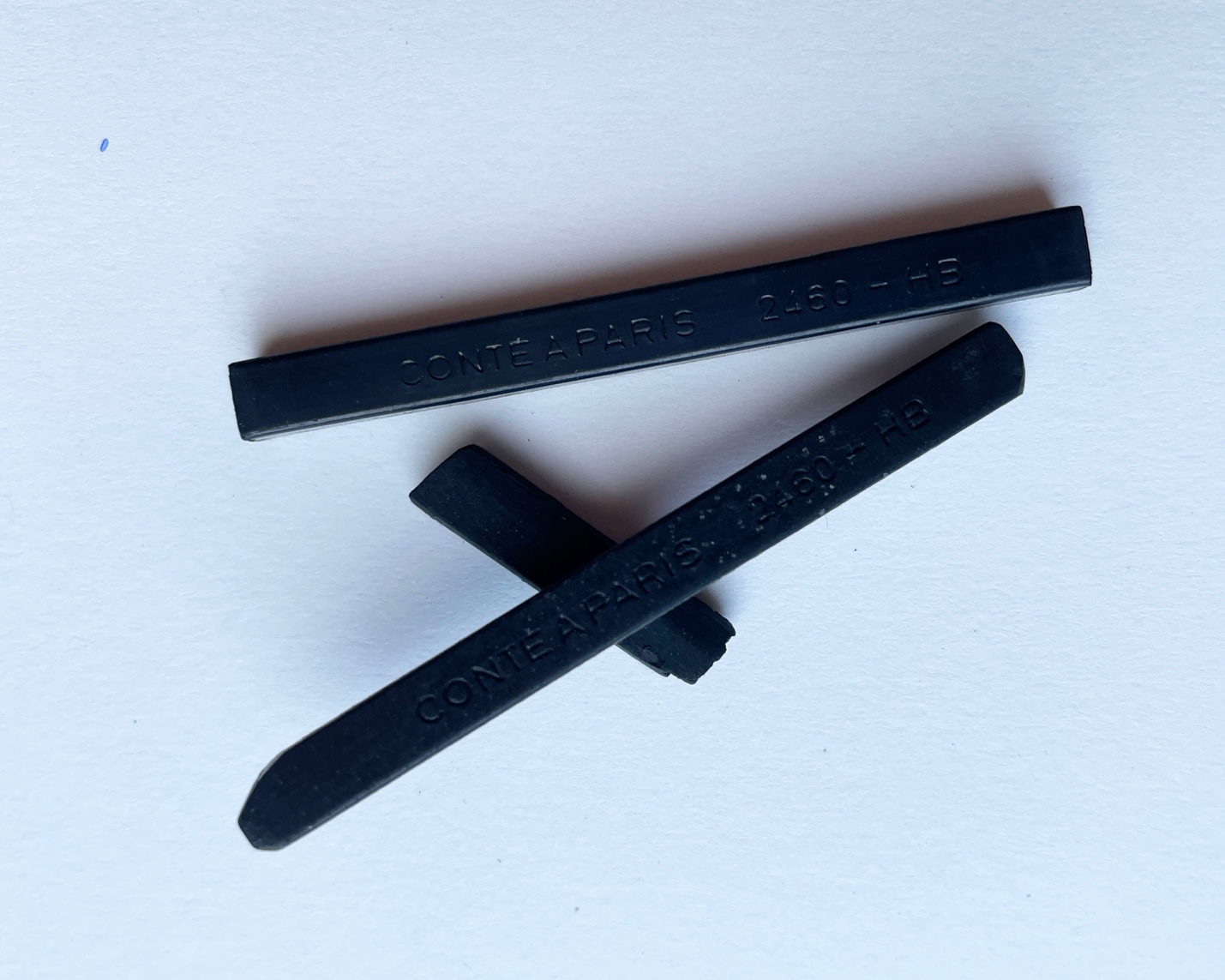

ahaney CC BY-SA 3.0
Graphite – the accidental production of graphite occurred when Edward Acheson was it experimenting with carborundum. When baked at an extremely hot temperature carborundum will vaporize and leave behind graphite.
Drawing Basics: Understanding Pencil Grades
Faber-Castell: wood cased pencil production
How to hold and control your pencil
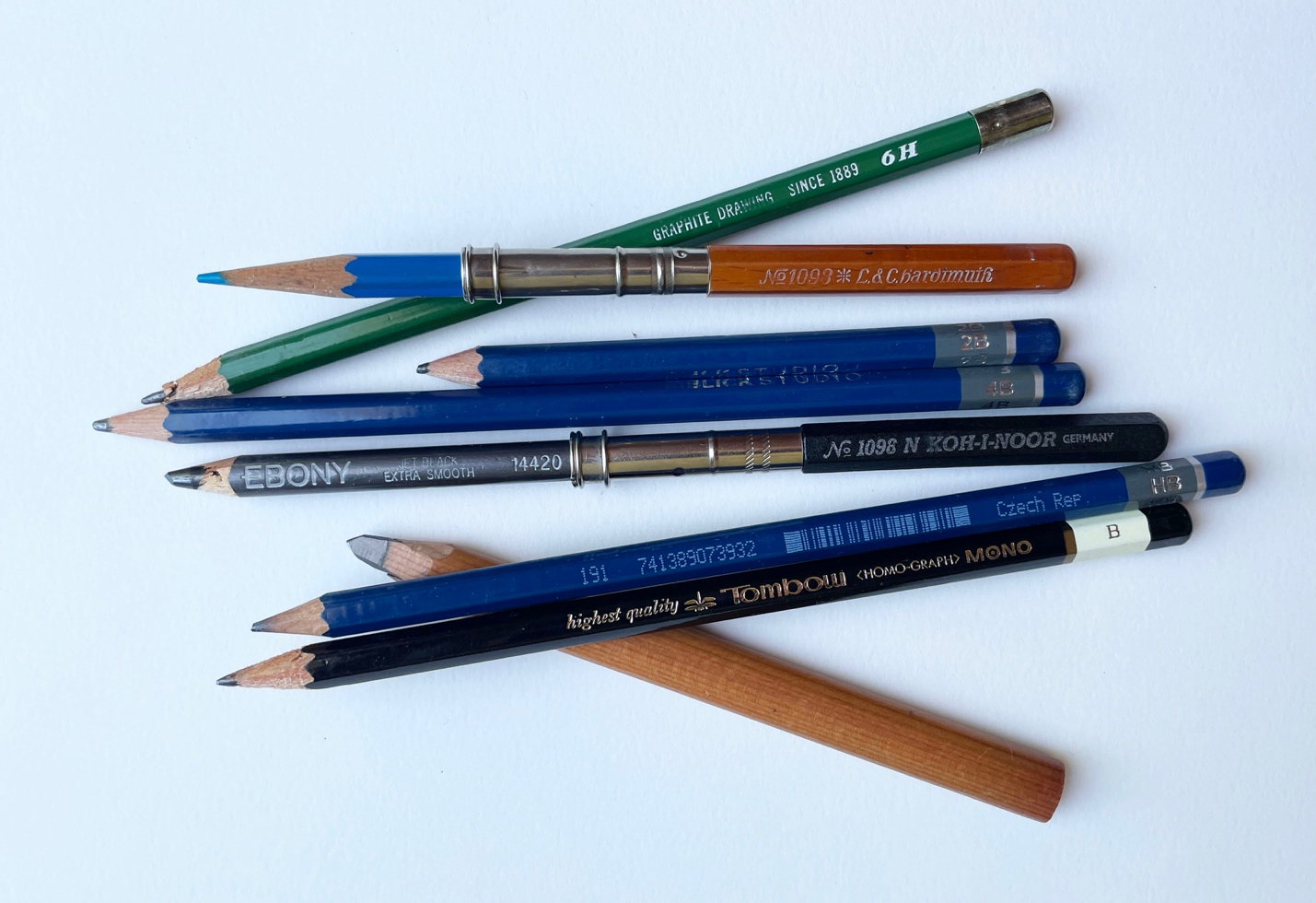

ahaney CC BY-SA 3.0
Ink – there are four types of ink that created from natural materials. Lamp black is the most typical but there’s also carbon black, purple-black iron gall, blue-black logwood, and brown bistre. There are various devices used when drawing with ink for example, a nib and handle, brush, or technical pen.
The MET: How a drawing is made.
How to shade with pen and ink.
Pen & Ink Drawing Tutorials – How to shade simple forms with cross hatching.
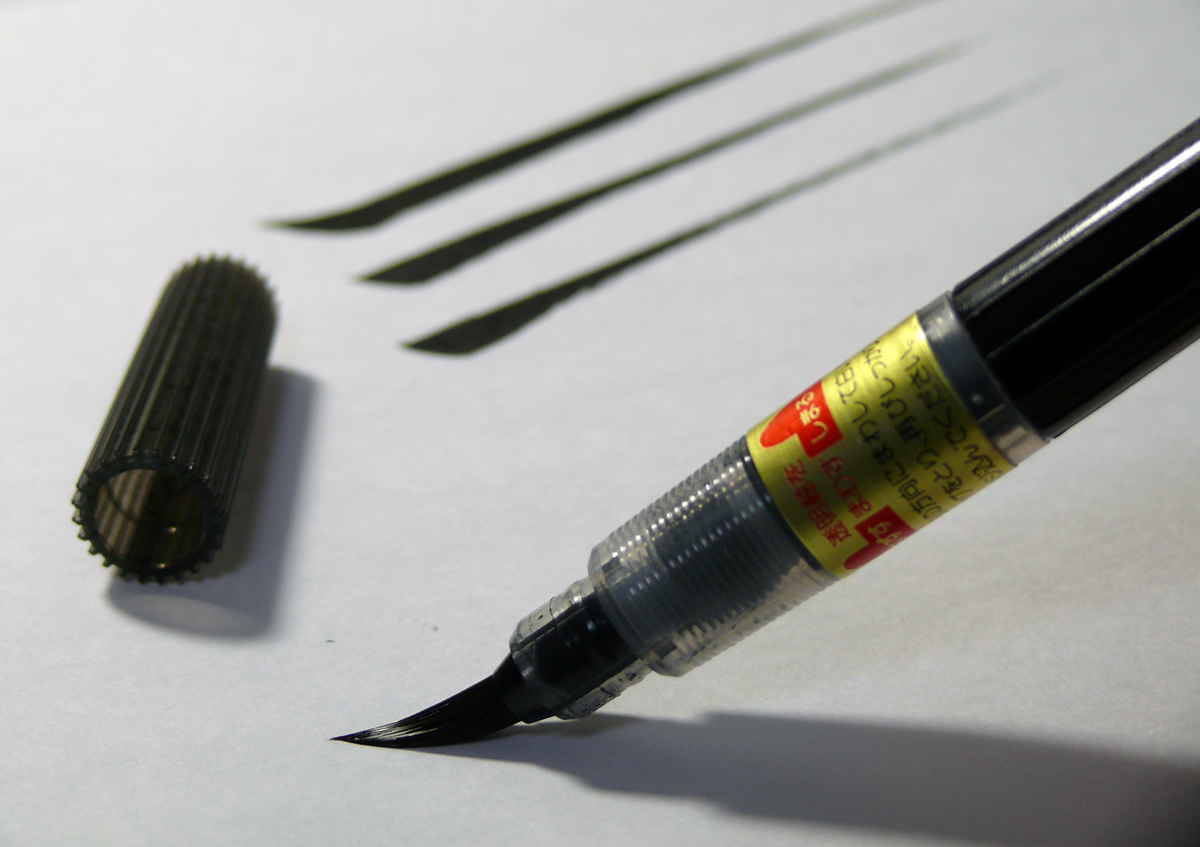

I, Avenafatua CC BY-SA 3.0
Dry Pastel – sticks of pastels are created by mixing a gum binder, filler (to make it a paste), and dry pigment. Variables in the quality of the ingredients will change the consistency and look of the marks. 12 Soft Pastel Techniques for every artist
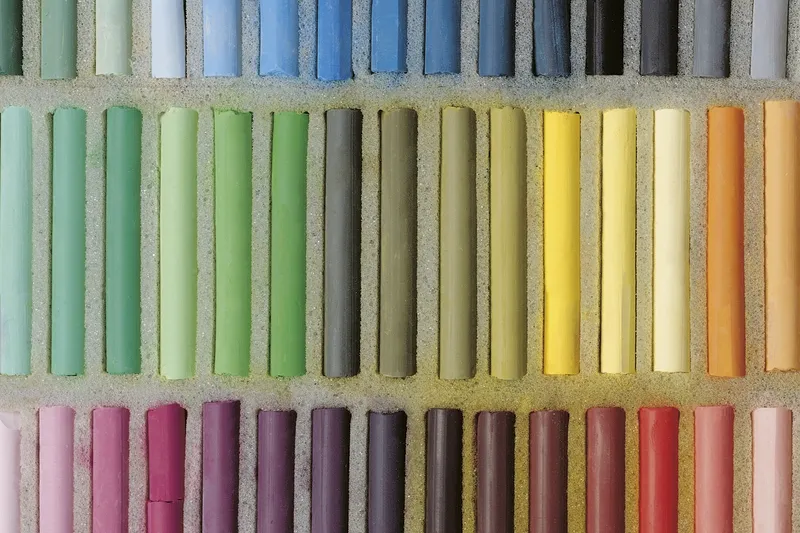

Oil pastel – is has a different feel and appearance than dry pastel because of the binder used in production. Oil pastels are made with pigments, non-drying oil, and wax. Unlike regular crayons that we know, oil pastels stay loose, easily malleable, and dry slowly. The 6 best techniques using oil pastel

ahaney CC BY-SA 3.0
Color pencils – colored pencil, pencil crayon, or colored lead is an art medium constructed of a narrow, pigmented core encased in a cylindrical wooden case. Colored pencils’ cores are wax or oil based and contain varying proportions of pigments, additives, and binding agents. 8 Things I wish I knew as a beginner.
Using Vaseline with colored pencils
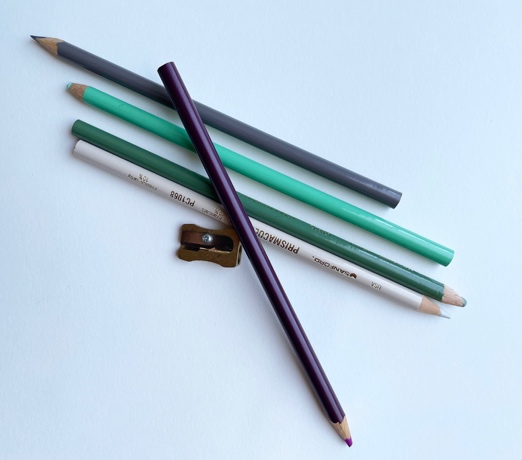

ahaney CC BY-SA 3.0
Erasers– an eraser is used for removing marks from paper, parchment, or vellum. Erasers have a rubbery consistency and come in a variety of shapes, sizes, and colors. Some pencils have an eraser on one end made from synthetic rubber and synthetic soy-based gum. Or some pencils come with specialized erasers are made from vinyl, plastic, or gum-like materials.
Several types of erasers:
Rubber – typically the pink erasers found on the end of a #2 pencil. How it has made
Gum – brown in color and easily break down.
Kneaded – gray and are best used with charcoal. 3 ways to use a kneaded eraser
Vinyl or plastic – an eraser, usually white.

ahaney CC BY-SA 3.0
Reverse drawing – is created with charcoal and typically a kneaded eraser. In reverse drawing, the surface area is first covered with an even layer of charcoal, then the artist begins their sketch with an eraser to establish highlights first. Contrast and tone are frequently adjusted and manipulated throughout the entire drawing process. Charcoal reverse drawing
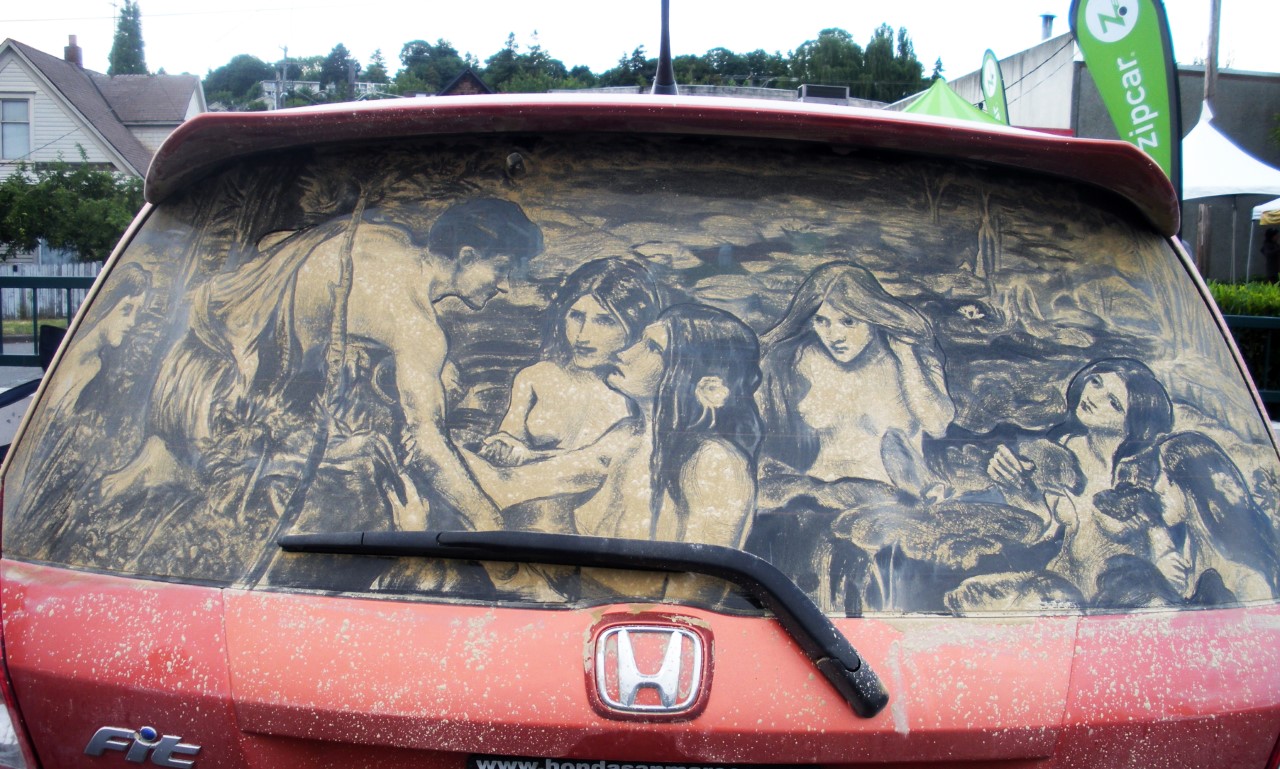

Figure 1 Reverse drawing of Waterhouse’s Hylas and the Nymphs by artist Scott Wade, who uses reverse drawing techniques on dusty car windows.
Blending stump and tortillon – are cylindrical drawing tools, tapered at the end and usually made of rolled paper. They are used by artists to smudge or blend marks made with charcoal, conté crayon, pencil, or other drawing utensils. A blending stump is tightly wrapped paper and is pointed at both ends. Tortillons produce slightly different textures than stumps when blending.
Cleaning of tortillons and stumps usually involves removing the used outer layer of paper by scraping or rubbing the implement on an abrasive surface, such as sandpaper, carpet, pink rubber erasers, or an emery board.
The basics of using blending stumps
How to clean old and dirty blending stumps
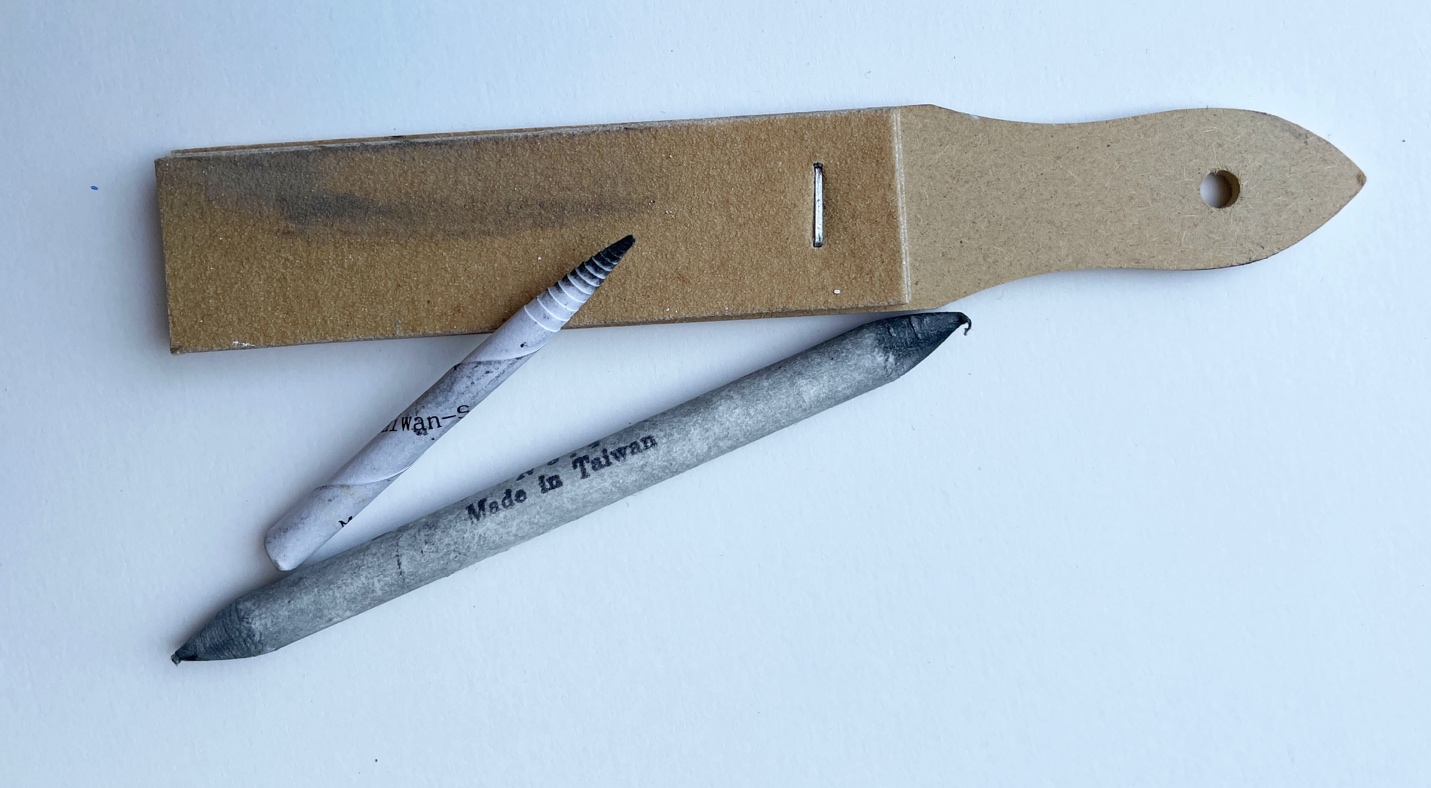

ahaney CC BY-SA 3.0
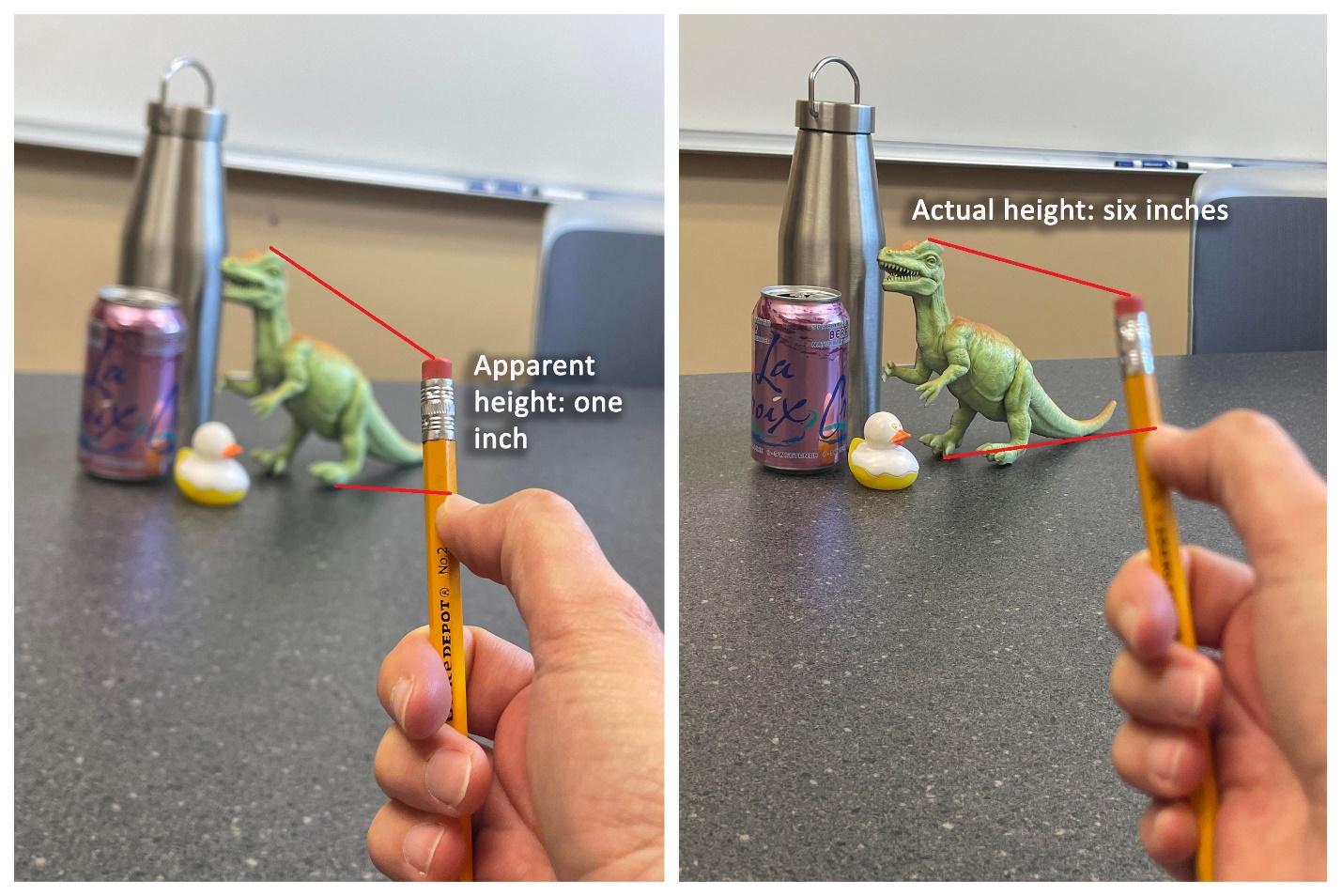
Sighting – is most useful when comparing objects and building uniform relationships within a composition. How to draw with sighting
Measuring with pencil for observational drawing
Sighting, Measuring, Mapping: MCAD
T square – also known as a t shaped ruler, is a useful tool used for mechanical or accurate drawing approaches. They are used to establish straight, even horizonal lines and can be guiding tool for a triangle to create vertical lines. The edge of a t square rests along the side of your tabletop as it slides along the top surface of your drawing paper. How to use a T square
Set square introduction – 30/60/90 and 45
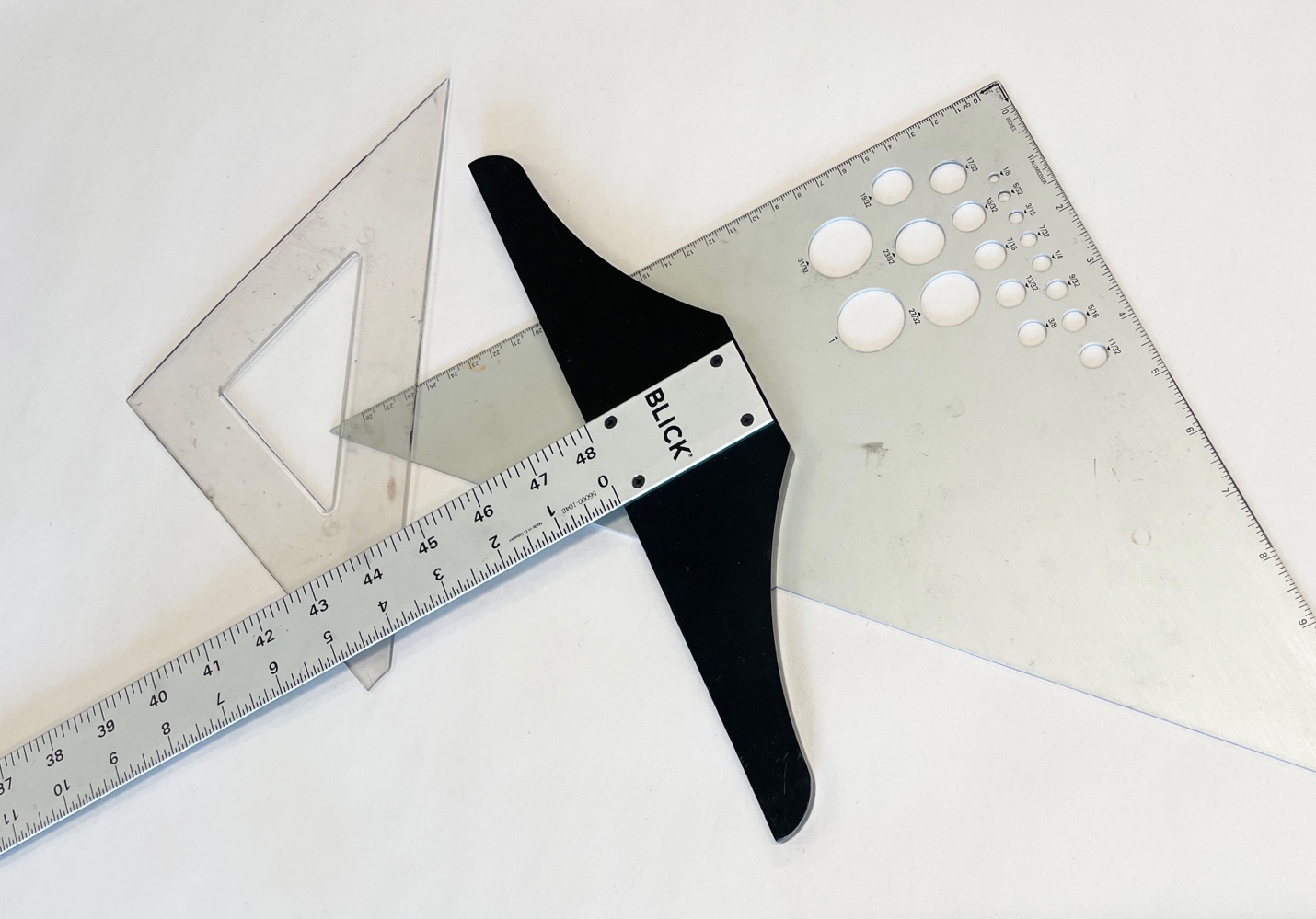
ahaney CC BY-SA 3.0
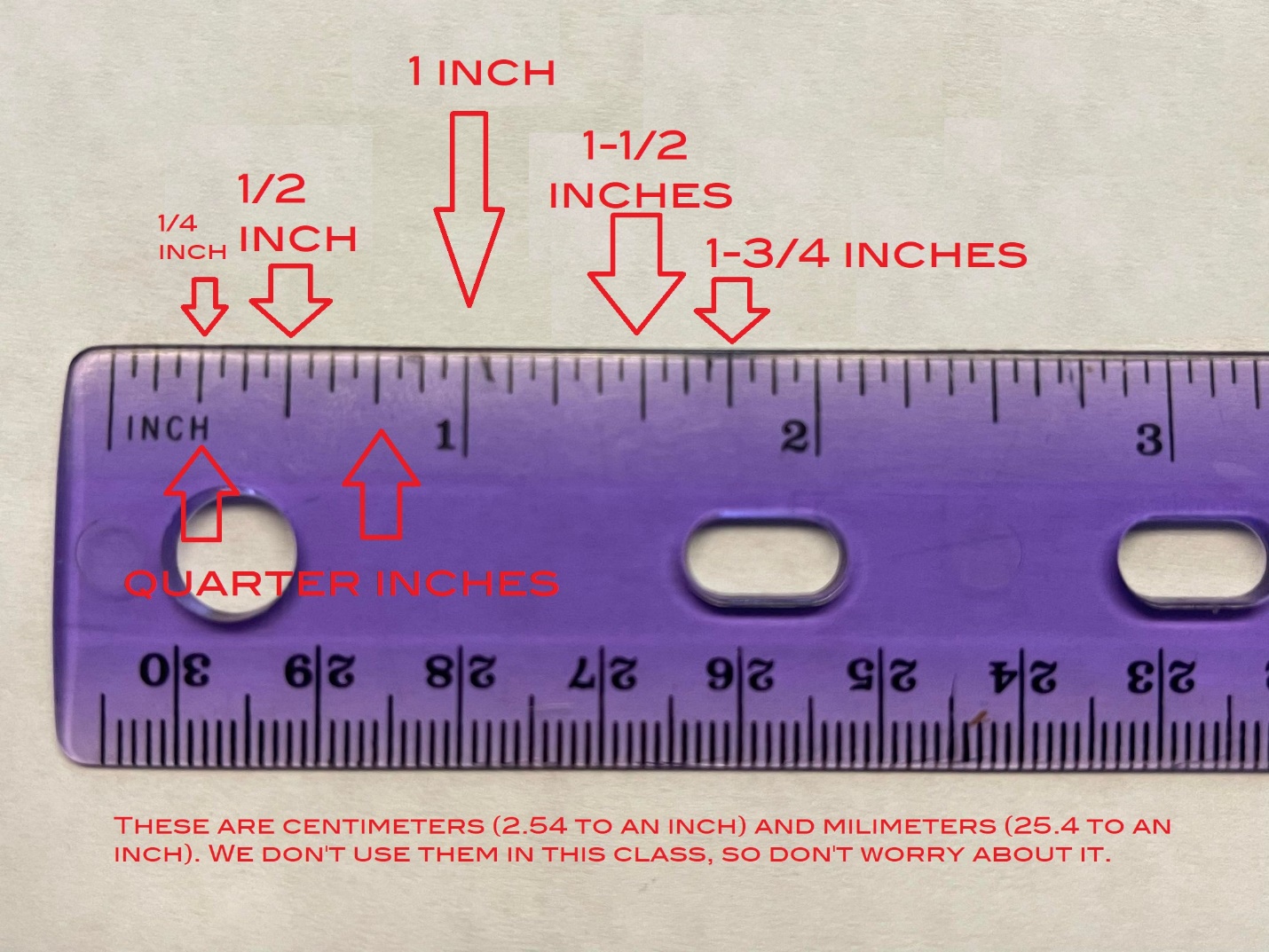
How to read a ruler – when making art it is vital to have the capacity to read a ruler with accuracy. Rulers are used for measuring, cutting, tearing, scoring, and drawing in general. How to read a ruler and tape measure
Compass – is a tool that helps draw perfect circles and arcs. When using a compass with numbers, you can use one to measure and mark distance in a work.
How to draw a circle (without a compass)
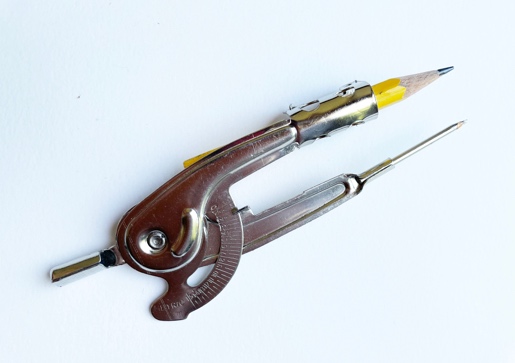
ahaney CC BY-SA 3.0
Grid transfer drawing – can be incredibly useful when transferring a photograph or image to larger surface like paper or canvas. By griding your reference and work surface, you can use each square to accurately depict proportions, architecture, and any type of subject matter. How to use a grid to draw and transfer images
Using pencil to transfer an image
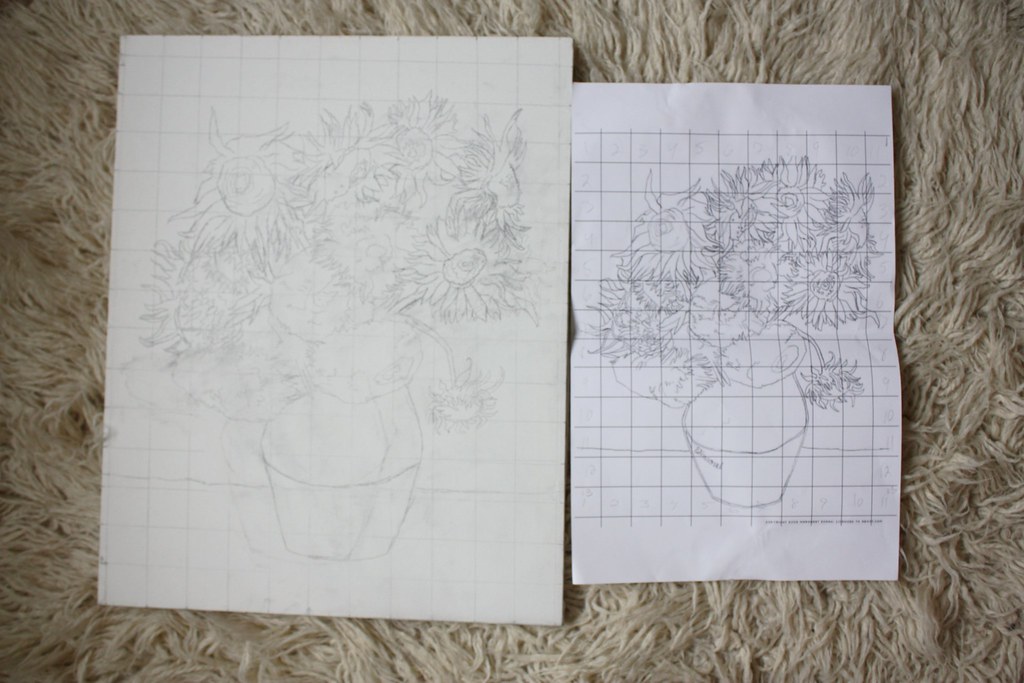
osirinthe Attribution-NoDerivs 2.0 Generic (CC BY-ND 2.0)
Plumb line – can help you find your vertical and horizontal lines accurately.
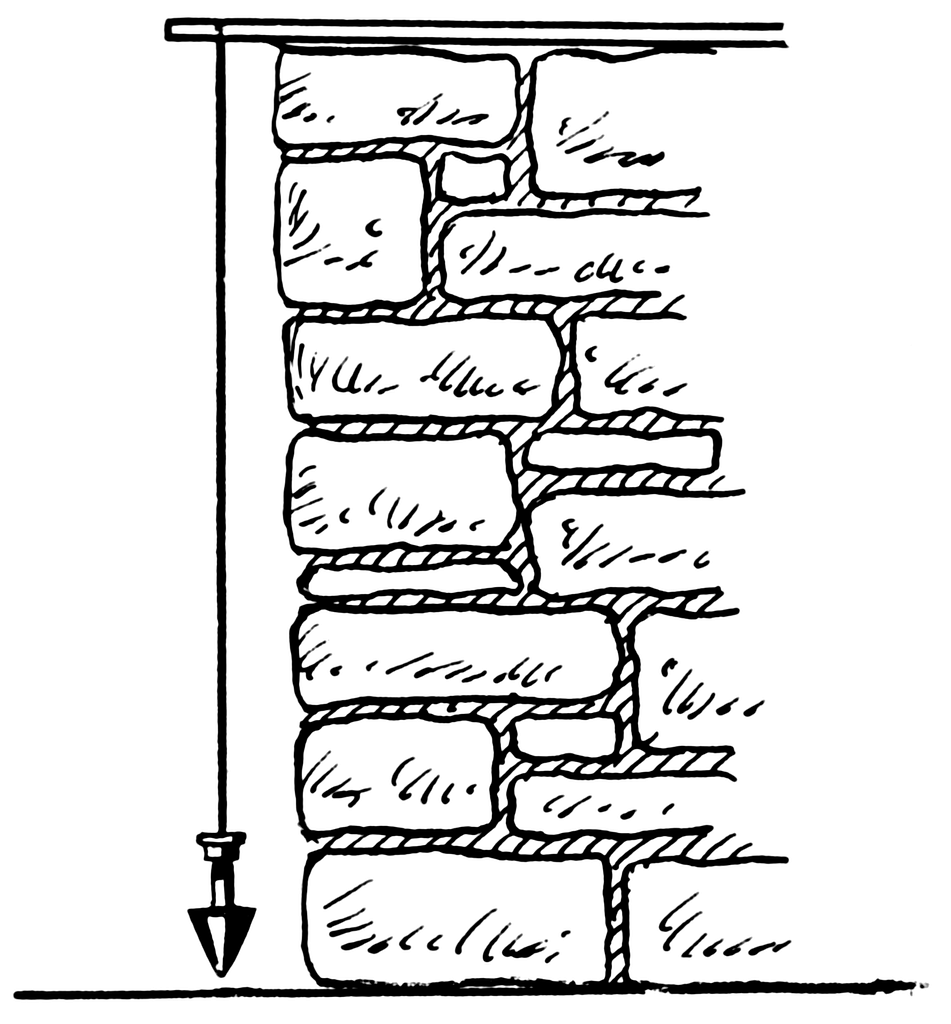
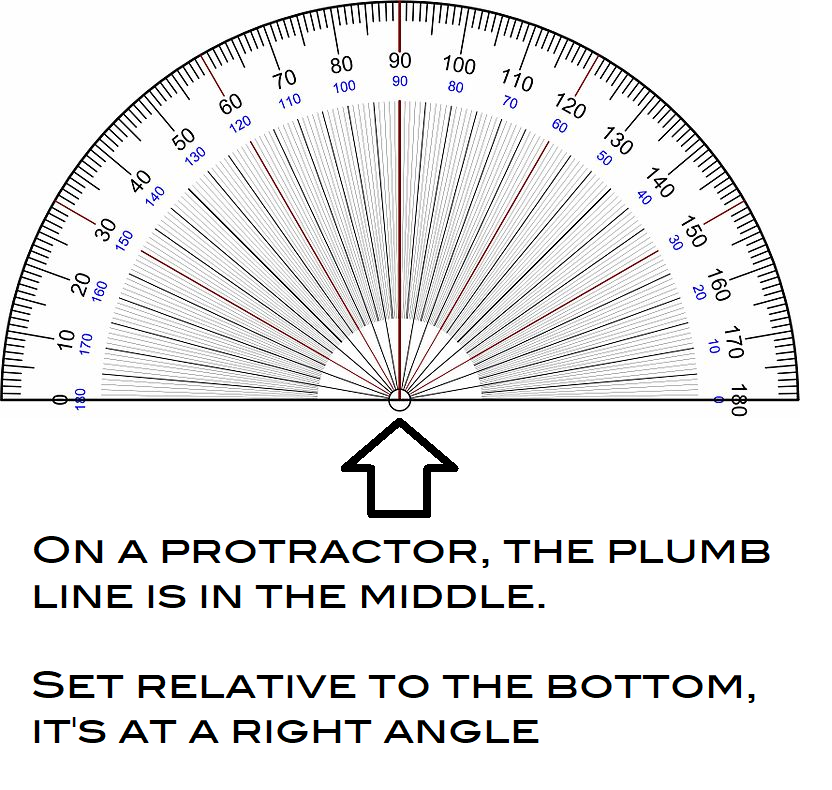
Viewfinder – a tool that helps artists crop a section or scene to arrange a composition. It is made of card stock or carboard and has a rectangular or square opening cut out of the center for the artist to look through.
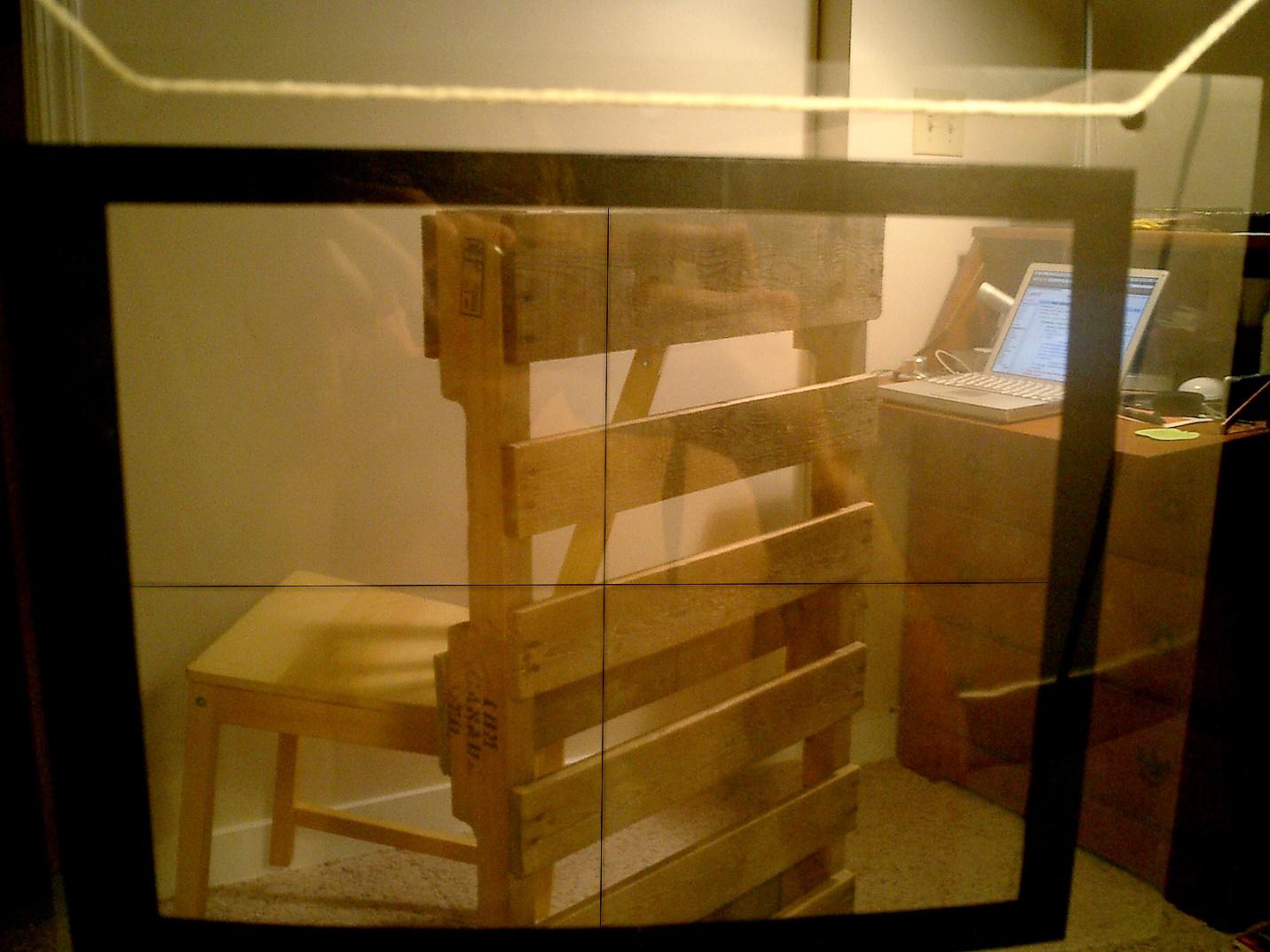

Figure 2 The view through a viewfinder. Credit: Bjorn Bulthuis CC BY SA 2.0.
Spray Fixative – a clear liquid that is sprayed or brushed on dry media to seal and stabilize the surface of the artwork. Spray Fixative

ahaney CC BY-SA 3.0
Thumbnail sketches – are quick small studies of objects or a subject matter used for preliminary practices. Thumbnails can help the artist find the most successful composition, locate highlights and shadows, and can be utilized for representations of larger works. What are thumbnail sketches
Thumbnail sketches: tips for drawing
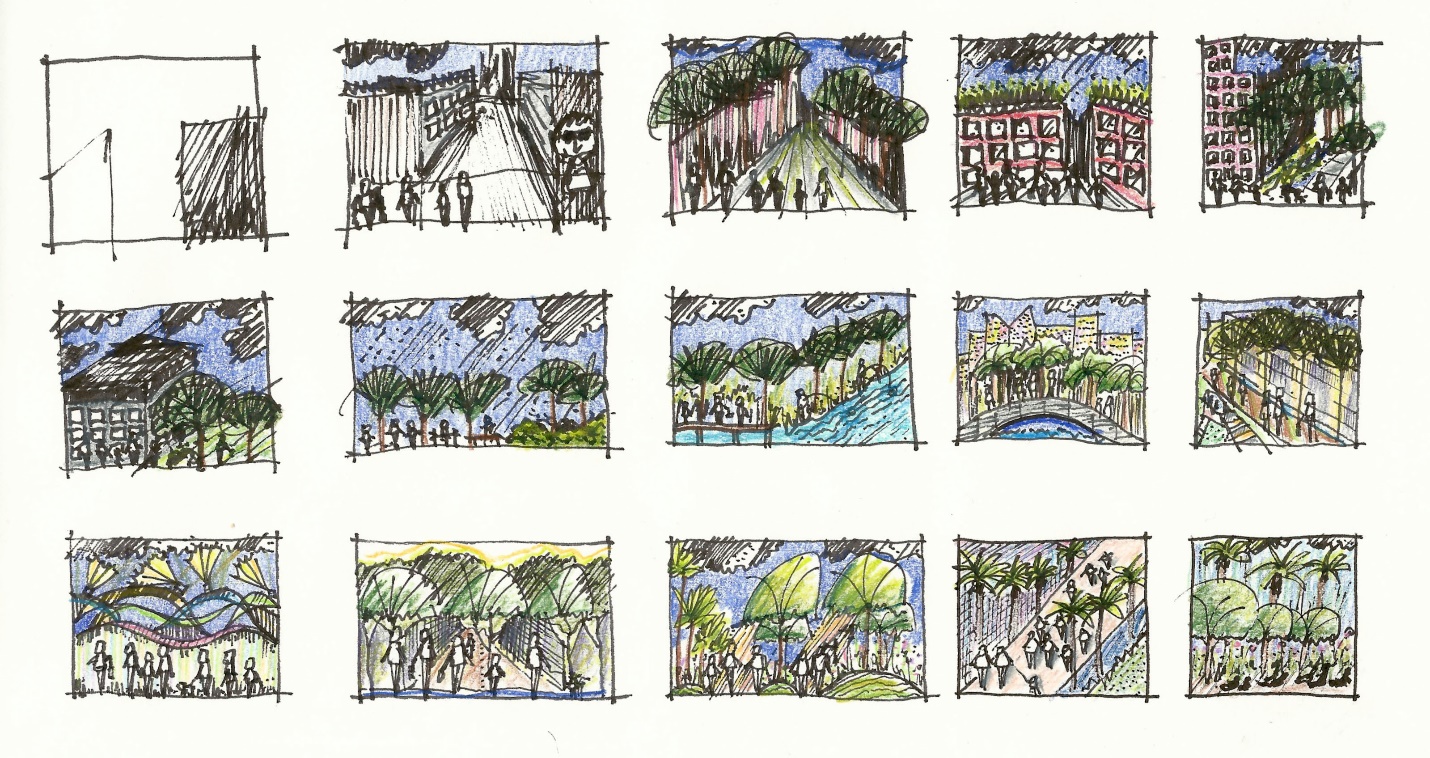
Credit: Brett Lezon, CC-BY-NC-SA.
The rule of thirds – is the understanding that segmenting a composition into sections will create an interesting image. Splitting a composition horizontally and vertically into thirds can give the artist landing points to place an object. This approach sets up dynamic compositions by avoiding placing an object in the exact center of a composition. The rule of thirds in art
The golden ratio vs. the rule of thirds

GIF demonstrating rule of thirds. Credit: Tadrart01, CC BY-SA 3.0.
Drawing & Painting: The Visual Instructor youtube
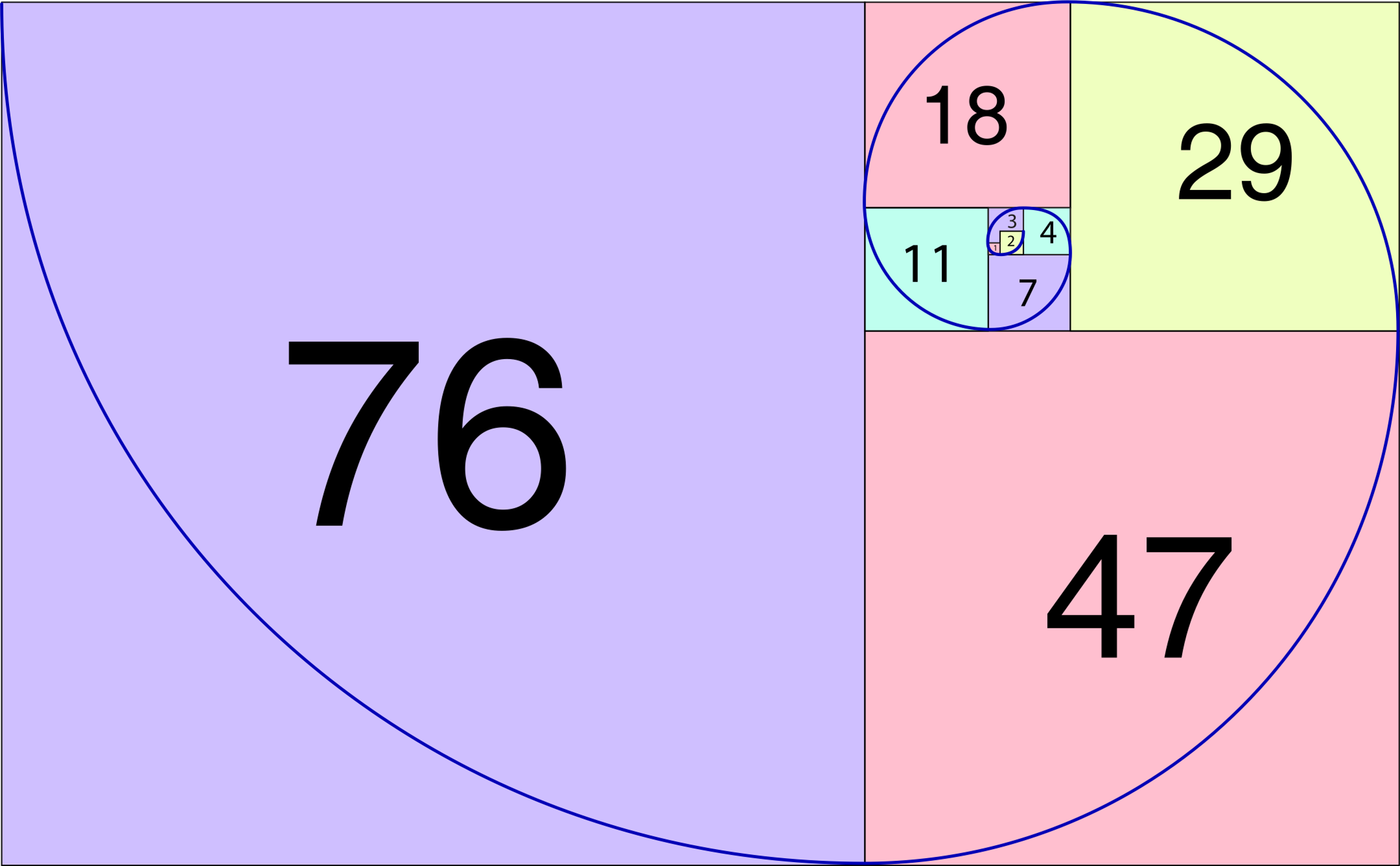
Golden ratio – is mathematic sequence where two quantities is the same ratio of their sum to the larger of the two quantities. It is also known as divine proportion.
Golden ratio for art beginners